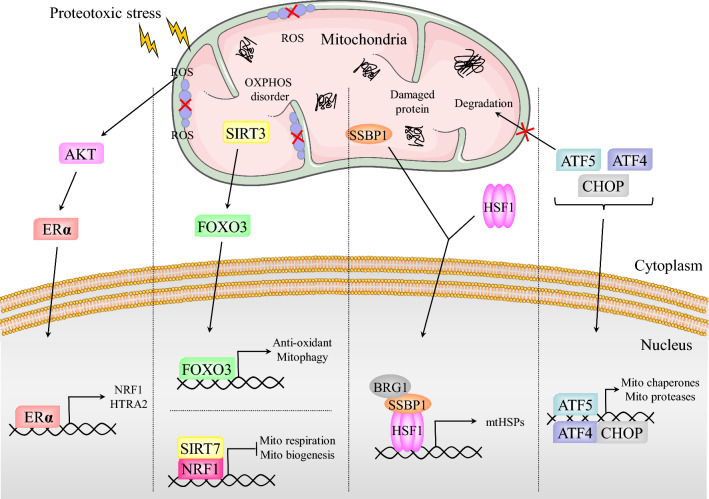
Fig. 2.
Mechanism of UPRmt in mammals. Upon ROS accumulation in IMS, the AKT-ERα axis is activated to trigger the transcription of NRF1 and HTRA2 in response to IMS damage. When ATF5 senses mitochondrial disorders, it translocates to the nucleus together with ATF4 and CHOP to synergistically promote the expression of mitochondrial chaperones and proteases. HSF1 forms a complex with SSBP1 and recruits the chromatin remodeling factor BRG1, consequently inducing the expression of mtHSPs. The SIRT3-FOXO3 axis is involved in antioxidant stress and mitophagy. The interaction of NRF1 and SIRT7 inhibits mitochondrial respiration and biogenesis, thereby reducing the load of damaged proteins. In summary, the mammalian UPRmt promotes mitochondrial recovery and maintains proteostasis through a variety of pathways