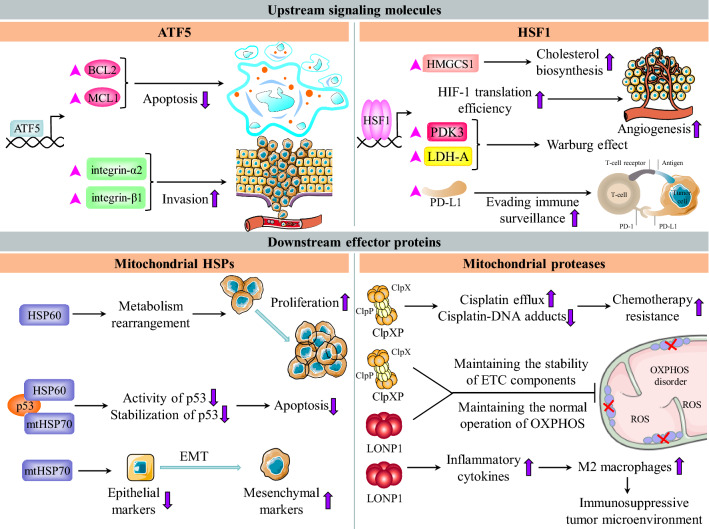
Fig. 3.
The roles of UPRmt components in cancer. The upstream signaling molecules of UPRmt play an important role in tumorigenesis. ATF5 transcribes BCL2 and MCL1 to inhibit cancer cell apoptosis. ATF5 upregulates integrin-α2 and integrin-β1 to promote invasion and migration. HSF1 suppresses the immune system by inducing PD-L1. HSF1 cooperates with PARP13 and PARP1 to repair the genome. The downstream effector proteins of UPRmt are conducive to the progression of cancer. HSP60 promotes the proliferation of cancer cells by regulating metabolic pathways such as glycolysis and the TCA cycle. mtHSP70 is involved in epithelial mesenchymal transition. HSP60 and mtHSP70 synergistically inhibit p53 to prevent it from exerting antitumor effects, thereby promoting the survival of cancer cells. ClpXP maintains the stability of mtDNA and genomic DNA, thus reducing the sensitivity to chemotherapy. LONP1 boosts the activation and M2 polarization of macrophages, thereby creating an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment. ClpXP and LONP1 coordinately regulate mitochondrial bioenergetics in cancer