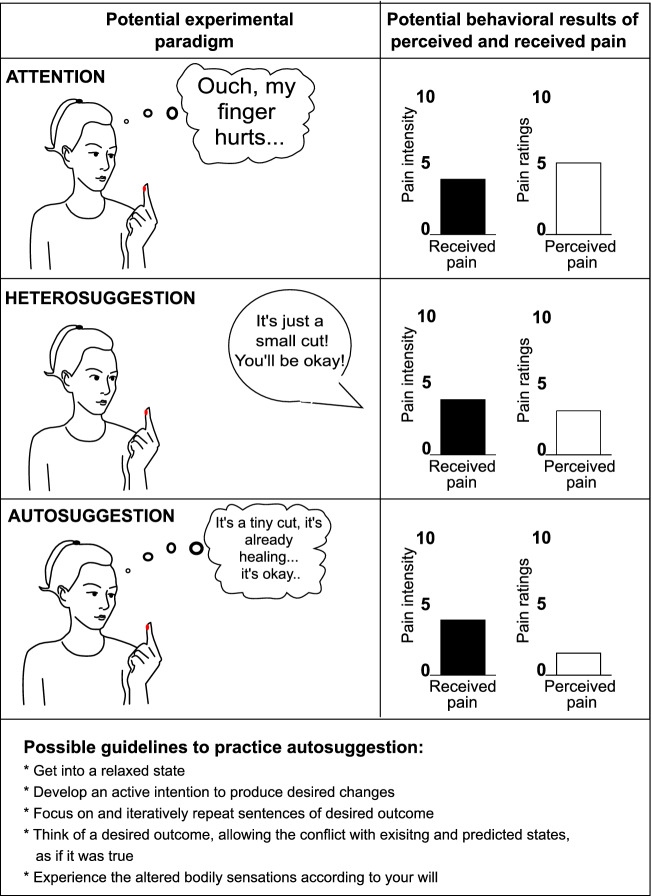
Fig. 1.
Conceptual representation of autosuggestion in a hypothetical comparison to attention and heterosuggestion in the context of a painful experience. Upper panel: The person directs attention to a painful experience at the finger. Ratings of perceived pain (white bars) are higher than the actual pain intensity (dark bars). Middle panel: The person experiences pain, and receives heterosuggestion from another person. Ratings of perceived level of pain are a bit lower than actual pain intensity. Lower panel: The person actively intends to reduce the perception of pain via autosuggestion. Ratings of perceived level of pain are significantly lower than actual pain intensity. Fourth panel: potential example guidelines to practice autosuggestion in an experimental setting