Fig. 6.
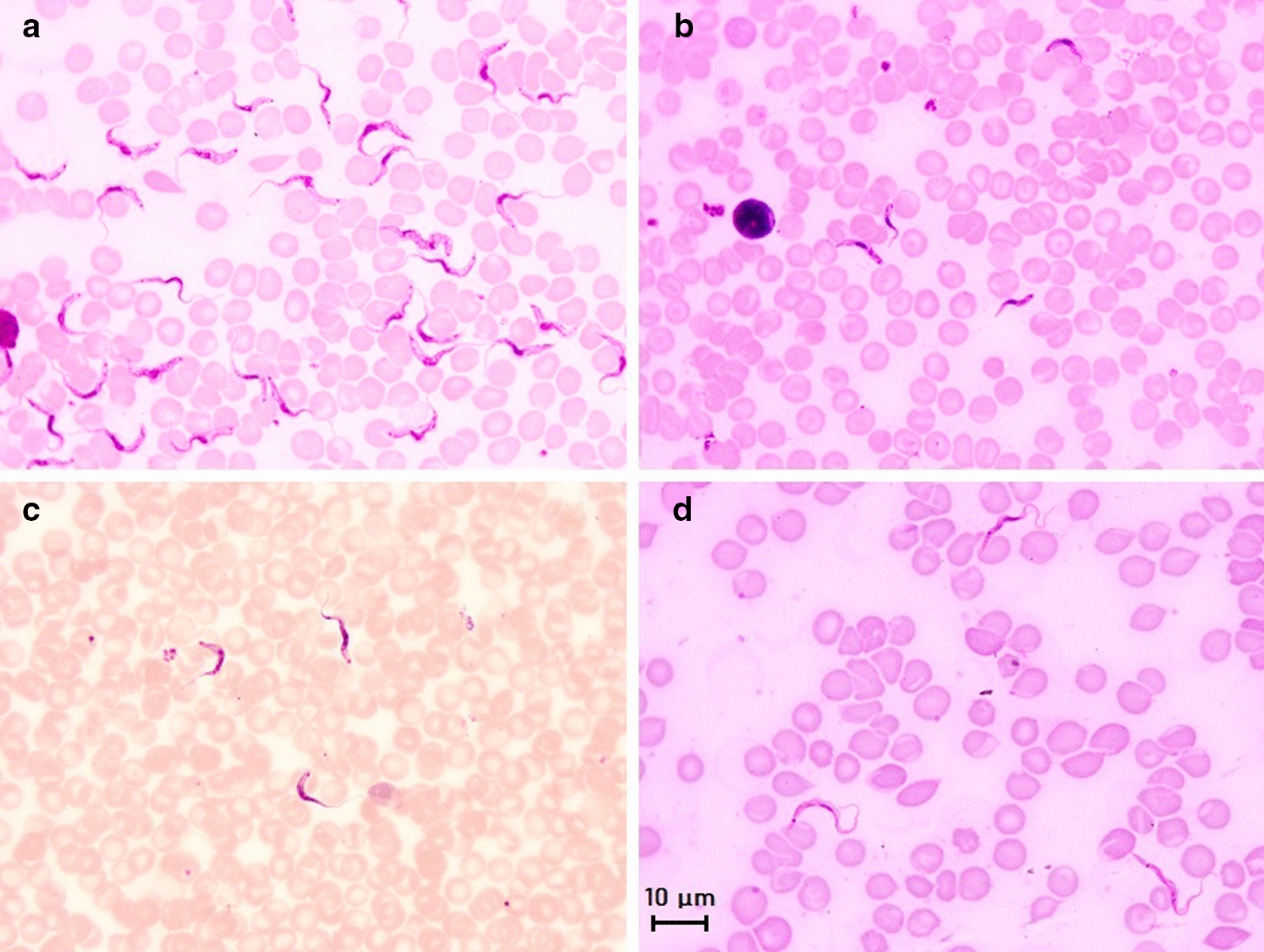
Main morphological features of four subgenera of mammal trypanosomes on Giemsa-stained thin blood smears. a Microscopic image of Trypanosoma brucei brucei in mice blood; morphology of the subgenus Trypanozoon: large-sized trypomastigote (17–30 µm), slender form, free flagellum, small sub-terminal kinetoplast, sharp posterior extremity, central nucleus and large undulating membrane; b Microscopic image of Trypanosoma congolense-type savanna in mice blood; morphology of the subgenus Nannomonas: small-sized trypomastigote (8–22 µm), no free flagellum, terminal sub-lateral kinetoplast, round posterior extremity, central nucleus and no undulating membrane. c Microscopic image of Trypanosoma vivax in cattle blood; morphology of the subgenus Duttonella: large-sized trypomastigote (20–27 µm), slender form, free flagellum, large terminal kinetoplast, round posterior extremity, central nucleus and large undulating membrane. d Microscopic image of Trypanosoma lewisi in rat blood; morphology of the subgenus Herpetosoma: very large-sized trypomastigote (21–36 µm), slender form, free flagellum, very large sub-terminal kinetoplast, very long sharp posterior extremity, anterior nucleus and large undulating membrane. Scale bar: 10 µm
