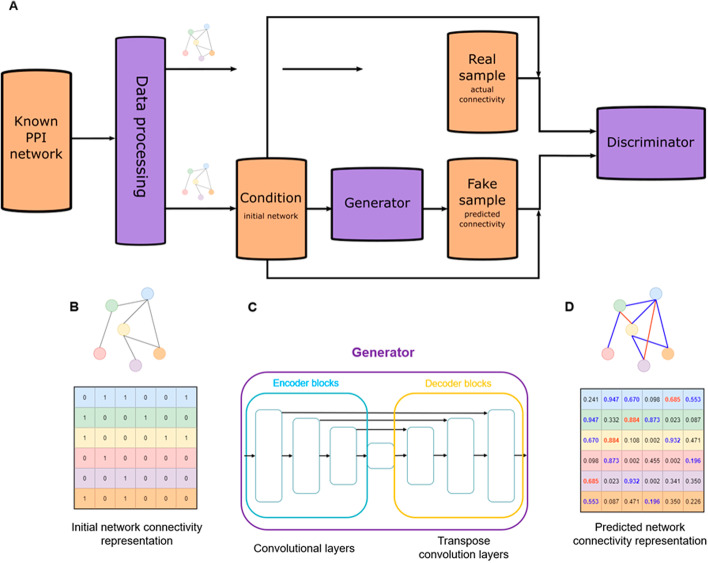
Fig. 3.
Machine learning. Schematic diagram of the conditional generative adversarial network (cGAN) architecture that uses the representation of the initial protein–protein interaction (PPI) network connectivity as condition with no input noise in the generator, and pairs of condition and real or generated connectivity representations in the discriminator (A) and simplified visualization of the prediction process (B–D). Input (sample condition) of the generator model is a representation of the initial connectivity via the adjacency matrix of the induced subgraph (B). Generator was implemented as a layer skipping concatenation method among the convolutional (encoder blocks) and transpose convolution (decoder blocks) layers (C). Output (fake sample) of the generator model is a representation of the predicted connectivity in the form of a confidence matrix, approximating the expected adjacencies in the given induced subgraph (D)