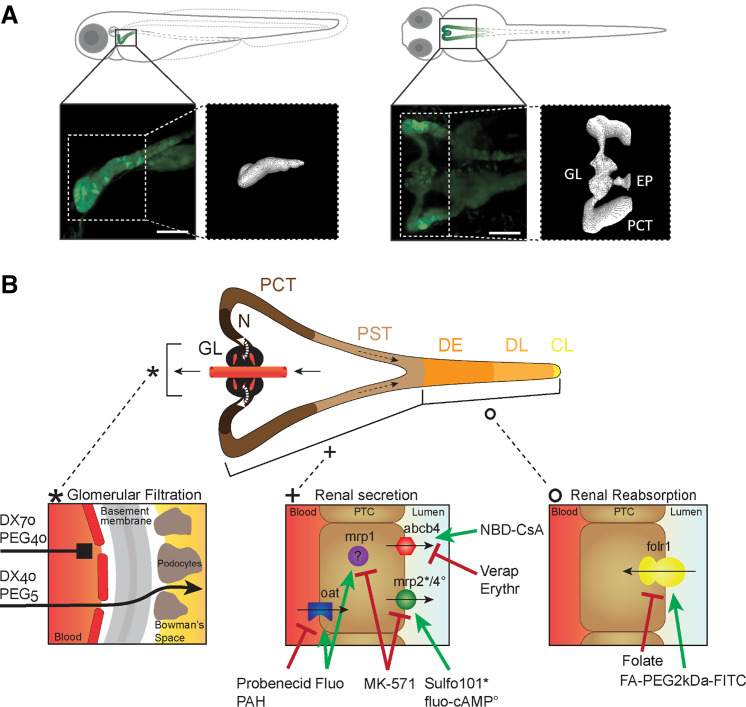
Figure 1.
Anatomic localization of the pronephros in a 72-h postfertilization (hpf) zebrafish larva (ZFL) and schematic representation of its functional units. A: lateral and ventral projection of a 72-hpf tg(wt1b:eGFP) ZFL expressing enhanced green fluorescent protein (eGFP) mainly in the proximal convoluted tubule (PCT) and glomerulus (GL). A faint signal was also present in the exocrine pancreas (EP). A three-dimensional projection of the pronephros is shown. Scale bars = 50 µm. B: the pronephros consists of two nephrons with a fused GL, neck (N), PCT, proximal straight tubule (PST), distal early (DE), late distal (DL), and collecting duct and cloaca (CL). Renal function encompasses glomerular filtration (left), renal secretion (middle), and renal reabsorption (right). Transporters are listed together with their substrates (green label) and inhibitors (red label) used in this study. abcb4, zebrafish homolog of human MDR1; DX, dextran; Erythr, erythromycin; FA, folate; Fluo, fluorescein sodium salt; folr1, folate receptor 1; mrp, multidrug resistance-associated protein; NBD-CsA, NBD-labeled cyclosporin A; oat, organic anion transporter; PAH, p-aminohippurate; PEG, polyethylene glycol; PTC, proximal tubule cell; Sulfo101, sulforhodamine 101; Verap, verapamil hydrochloride.