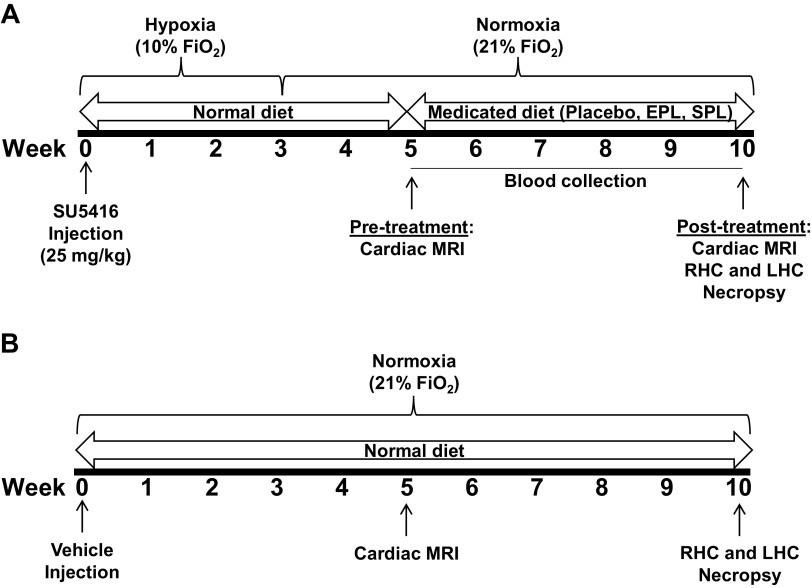
Figure 1.
Study timeline. A: male Sprague–Dawley rats (N = 48) were subcutaneously injected with SU5416 (25 mg/kg), exposed to hypoxia (10% ) for 3 wk and then returned to normoxia for 7 wk (referred to as SuHx rats). Pretreatment cardiac MRI (n = 43; n = 5 SuHx rats died before MRI) was performed at the end of week 5 followed by blood collection. Animals were then randomly assigned to receive medicated diets containing either eplerenone (EPL; 100 mg/kg/day; n = 15), spironolactone (SPL; 40 mg/kg/day; n = 15), or placebo (n = 13) from weeks 6–10. B: separate from the SuHx group, age-matched male Sprague–Dawley rats subcutaneously injected with vehicle alone and maintained in normoxic conditions underwent cardiac MRI (n = 4; end of week 5), cardiac catheterization, and necropsy (n = 4 for both at the end of week 10). Tissue was obtained in additional normoxic control animals at the end of 10 wk for RV (n = 9) and lung (n = 6) mRNA expression. LHC, left heart catheterization; RHC, right heart catheterization.