Figure 7.
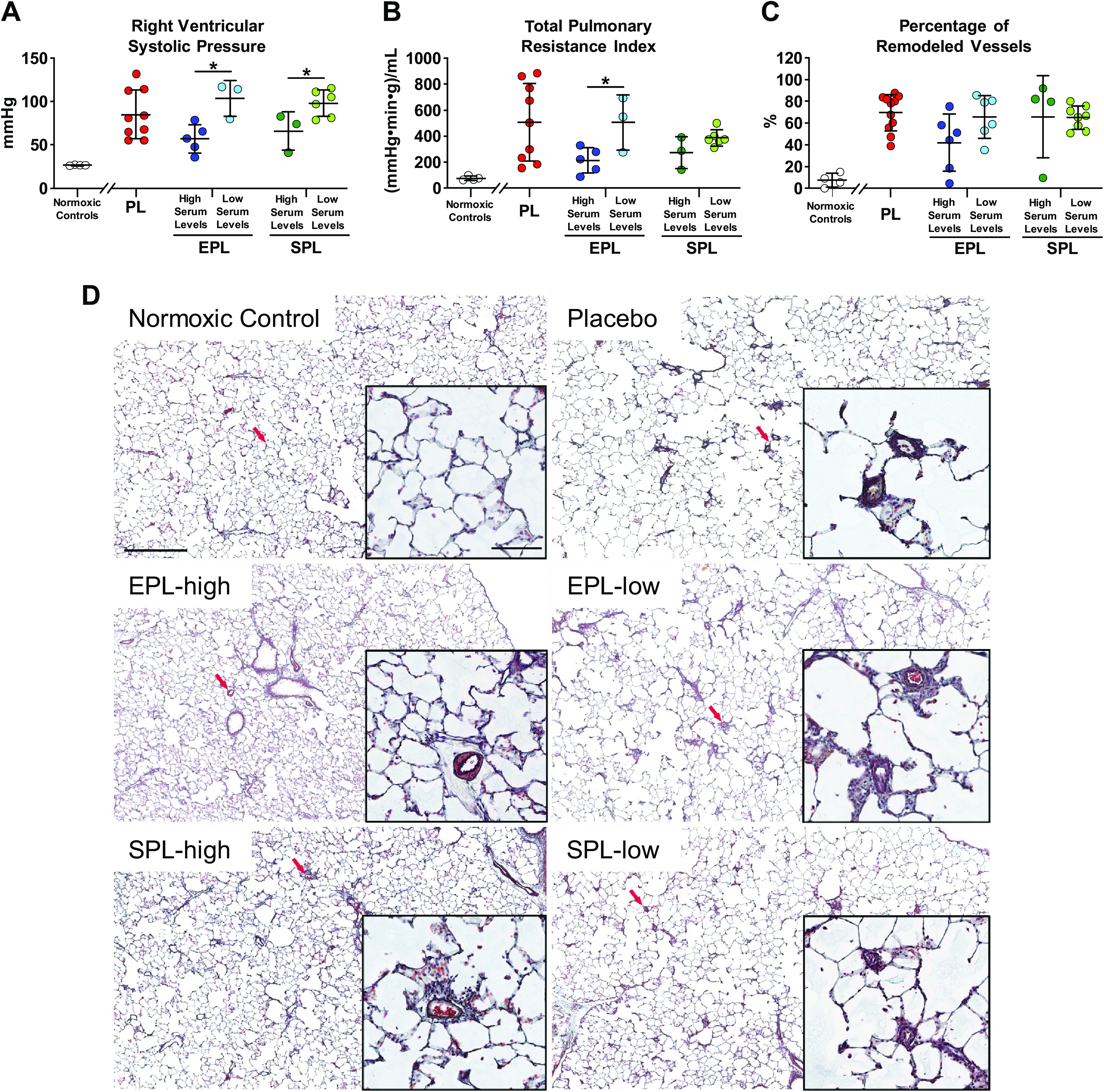
Treatment with mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists had a concentration-dependent effect on right ventricular systolic pressure (RVSP) and total pulmonary resistance index (TPRI) but not pulmonary vascular remodeling. A: RVSP was not significantly different between the three treatment groups (P = 0.15). However, in eplerenone (EPL)- and spironolactone (SPL)-treated animals, those with serum drug concentrations above the mean (high serum levels) had lower RVSPs compared to animals with drug concentrations below the mean (low serum levels; P = 0.02 and 0.04, respectively). RVSP was not successfully measured in some placebo- (n = 2), EPL- (n = 4), and SPL-treated (n = 3) animals. B: TPRI was also not significantly different between the three treatment groups (P = 0.24); however, EPL-treated animals with serum drug concentrations above the mean had lower TPRI compared with those with drug concentrations below the mean (P = 0.05). In contrast, there was a nonsignificant trend of lower TPRI in animals with high compared with low serum levels in the SPL treatment group (P = 0.09). C: pulmonary artery remodeling as defined as the percentage of grade 1 + 2 occlusion of small pulmonary arterioles (diameter < 100 µm; see methods and Supplemental Fig. S1B for details) was also not significantly different across the three treatment groups (P = 0.19). The percentage of remodeled vessels tended to be lower in animals with high versus low serum EPL concentrations (P = 0.09), whereas it was similar in SPL-treated animals with high versus low concentrations (P = 0.47). Data are presented as means ± SD of 8–9 animals per group for RVSP and TPRI, and 11–12 animals per group for histologic grading of vessel occlusion. One-way ANOVA was used to compare the three treatment groups and pooled t tests were used to compare the differences between the high and low serum level groups. Serum was collected between week 5 (pretreatment) and week 10. The mean concentration in each group was calculated based on measured concentrations after treatment initiation until prior to cardiac catheterization (weeks 6–9). See Fig. 4 for all measured concentrations. Normoxic controls (n = 4) are shown for comparison. *P ≤ 0.05. D: representative images of lung vessel histomorphology in a normoxic control (top left) and SuHx animals treated with either placebo (top right), EPL (high serum level: middle row, left; low serum level: middle row, right) or SPL (high serum level: bottom left; low serum level: bottom right). Red arrows indicate location of higher magnification image in inset. Scale bar: 500 and 100 µm (inset). PL, placebo.
