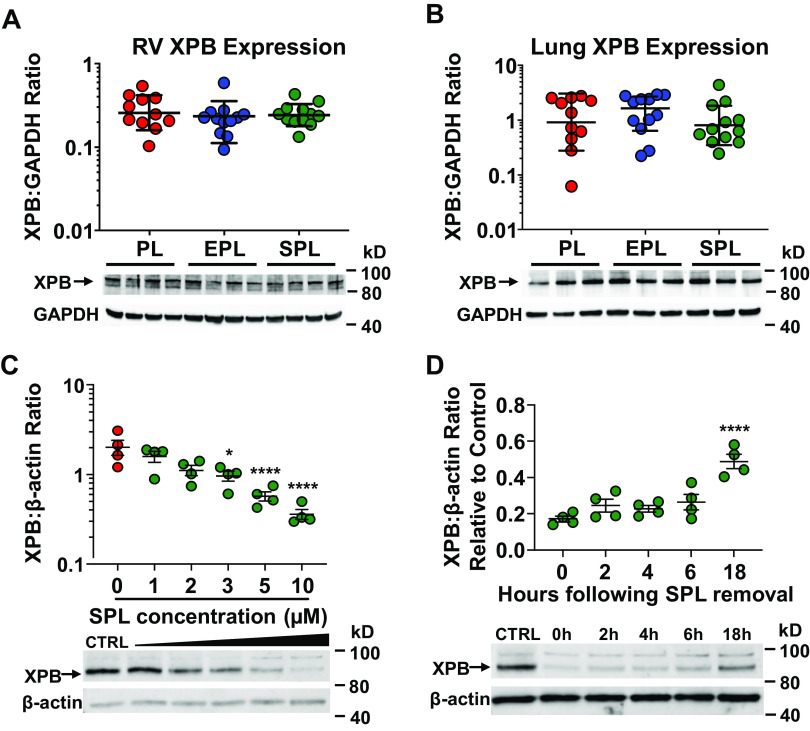
Figure 9.
Right ventricular (RV) and lung XPB protein expression is preserved in spironolactone (SPL)-treated SU5416-hypoxia (SuHx) rats. Protein expression of XPB in the RV (A) and lung (B) was not significantly different between the three treatment groups (P = 0.51 and P = 0.53). Tissue homogenates from the RV free wall and the caudal lobe of the right lung were resolved by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted for XPB and GAPDH. In A and B, one-way ANOVA was used to compare the three treatment groups. C: XPB protein levels in primary human pulmonary artery endothelial cells (PAECs) were dose dependently reduced by SPL (P < 0.0001 for the slope of the dose-response curve). *P < 0.05, ****P ≤ 0.0001 for the pairwise contrasts of SPL treatment compared with vehicle control (CTRL). Whole cell lysates from PAECs were collected after a 2-h incubation with vehicle CTRL (DMSO) or increasing doses of SPL, resolved by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted for XPB and β-actin. D: XPB levels in PAECs return to approximately 50% of baseline 18 h after SPL treatment in vitro. ****P < 0.0001 for the difference in XPB protein levels 18 h after SPL removal compared with 0 h. PAECs were treated with SPL (10 µM) for 2 h followed by replacement of the cell culture media with fresh media without SPL. Whole cell lysates were then collected at 0, 2, 4, 6, and 18 h after the media was changed, resolved by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted for XPB and β-actin. Representative Western blots are shown below each of the densitometry plots. In C and D, dose- and time-dependent effects of SPL were analyzed by fitting a linear regression line. One-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s test was used to examine the effect of each dose and time point.