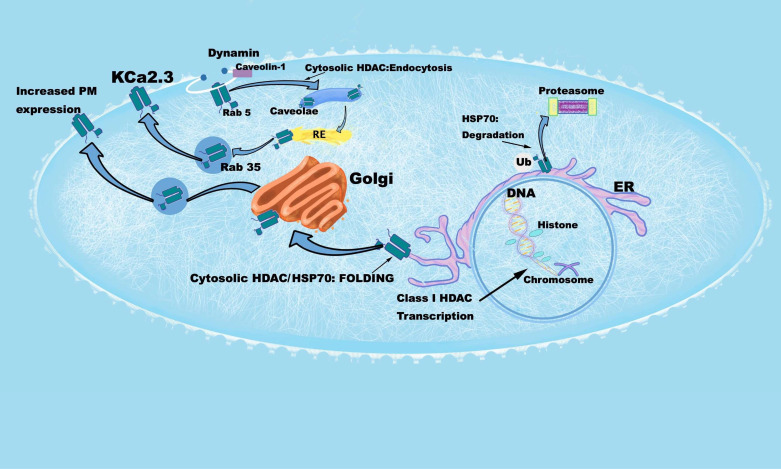
Figure 10.
Cell model illustrating effects of HDACi on KCa2.3 transcription, folding, trafficking, and plasma membrane expression. Starting in the nucleus, an increase in histone acetylation by HDACi results in increased transcriptional expression of KCa2.3. HDACi also increases HSP70 expression which facilitates the folding of KCa2.3. Inhibition of HSP70 by VER155008 results in degradation of KCa2.3, presumably in the proteasome. Inhibition of dynamin- and Rab5-dependent KCa2.3 endocytosis by HDACi would result in an increase in KC2.3 plasma membrane (PM) expression. Whether this is a direct result of increased tubulin acetylation or acetylation of KCa2.3 remains to be elucidated. The effects of HDAC inhibition on the Rab35-dependent recycling and Golgi-to-PM trafficking of KCa2.3 remain to be determined. HDACi, histone deacetylase inhibitors; KCa2.3, calcium-activated potassium channel.