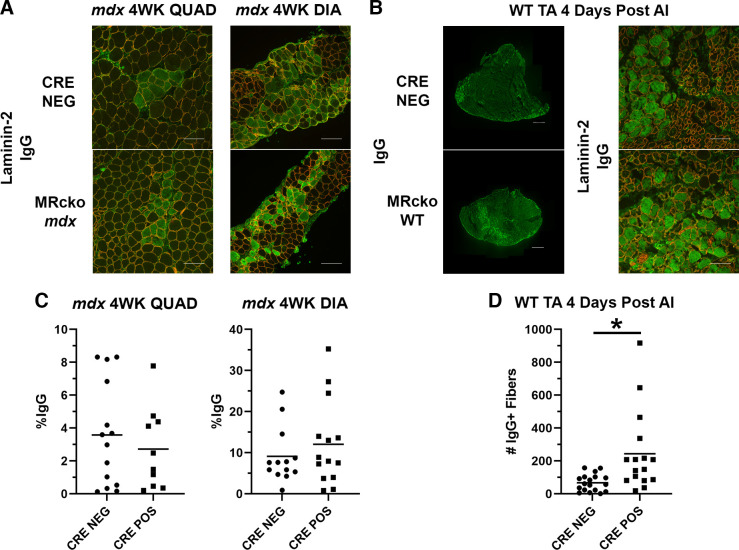
Figure 6.
Myofiber degeneration in 4-wk-old (4WK) myeloid mineralocorticoid receptor knockout (MRcko) mdx skeletal muscles and MRcko wild-type (WT) tibialis anterior muscles (TAs) 4 days after acute injury (AI). A: representative merged images of 4-wk-old MRcko mdx quadriceps (QUAD) (n: MRcko = 6 M, 4 F; Cre− = 7 M, 7 F) and diaphragms (DIA) (n: MRcko = 6 M, 8 F; Cre− = 3 M, 10 F) and mdx Cre− controls stained for immunoglobulin G (IgG, green) and laminin-2 (red) to visualize and quantify degenerating myofibers. Scale bars, 100 µm. B: representative composite IgG images of MRcko WT TAs 4 days after acute injury (n: MRcko = 9 M, 7 F; Cre− = 8 M, 9 F) and zoomed representative IgG and laminin-2 merged images. Composite scale bars, 500 µm; zoomed scale bars, 100 µm. C: quantification of tissue area from 4-wk-old MRcko mdx quadriceps and diaphragm muscles containing IgG staining (%IgG) compared with mdx Cre− controls. D: the number of IgG+ fibers in MRcko WT TAs 4 days after acute injury compared with WT Cre− controls. Data displayed in dot plots with mean horizontal line and x-axes labeled with “CRE NEG” for control and “CRE POS” for MRcko. Student’s t test: *P ≤ 0.05.