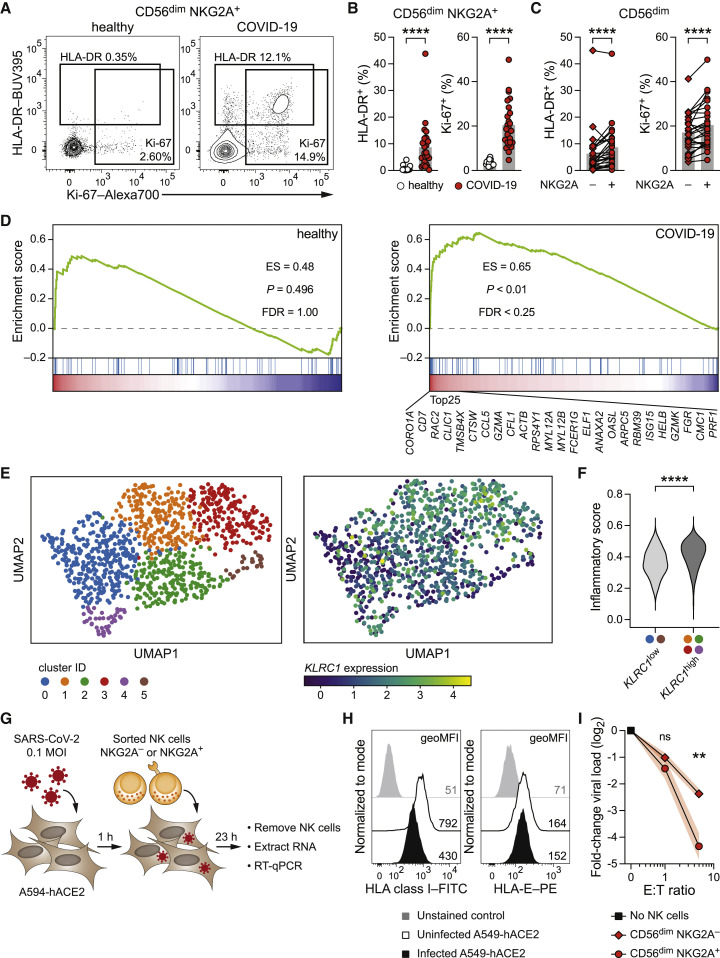
Figure 4.
NKG2A+ NK cells are activated in patients with COVID-19 and proficiently suppress SARS-CoV-2 replication in vitro
(A–C) Ex vivo Activation of NKG2A+ NK cells in the blood of healthy controls and of patients with COVID-19 as determined by flow cytometric detection of the activation marker HLA-DR and the proliferation marker Ki-67. (A) Representative expression of HLA-DR and Ki-67 by CD56dim NKG2A+ NK cells. Left: healthy control. Right: patient with COVID-19. (B) Summaries of markers expressed by CD56dim NKG2A+ NK cells in controls and patients (n = 17 healthy controls and n = 25 patients). (C) Summaries of markers expressed by NKG2A− CD56dim and NKG2A+ CD56dim NK cells in patients (n = 25).
(D–F) Analysis of publicly available single-cell RNA sequencing data of ex vivo NK cells from BALF of healthy controls and patients with COVID-19 (Liao et al., 2020). (D) Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) of a signature of inflammatory responses (Table S2) (Yang et al., 2019) along with KLRC1 expression in NK cells from BALF. Left: healthy controls. Right: patients with COVID-19. The top 25 transcripts positively correlating with KLRC1 in BALF NK cells of patients with COVID-19 are depicted. (E) UMAP plot illustrating the distribution of BALF NK cells from patients with COVID-19. Left: colored according to Leiden clustering. Right: colored based on KLRC1 expression. (F) Inflammatory score expression between cells of the KLRC1low bin and the KLRC1high bin.
(G–I) A549-hACE2 human lung epithelial cells were infected with SARS-CoV-2 (isolate SARS-CoV-2/human/SWE/01/2020) at MOI = 0.1 and co-cultured with NK cells. (G) Schematic illustration of experimental setup. (H) Uninfected and SARS-CoV-2-infected A549-hACE2 cultured without NK cells were assessed for HLA surface expression by flow cytometry at 24 h post-infection. Left: HLA class. Right: HLA-E (representative results of two independent experiments). (I) A549-hACE2 were infected with SARS-CoV-2, followed by co-culture with sorted CD56dim NKG2A− and NKG2A+ NK cells at the indicated effector/target (E:T) ratios starting at 1 h post-infection as in (G). Virus copies in adherent A549-hACE2 cells were quantified at 24 h post-infection by RNA isolation and RT-qPCR using the CDC nCoV-2019 N1 assay. Data are expressed as fold-change to SARS-CoV-2-infected A549-hACE cultured without NK cells (n = 6 NK cell donors in 2 independent experiments).
Data are represented as mean and individual data points (B and C), distribution (F), or mean ± SEM (I). Statistical significance was tested using Mann-Whitney U test (B and C), Wilcoxon signed-rank test (F), or two-way repeated measures ANOVA with Bonferroni correction (I). ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001.