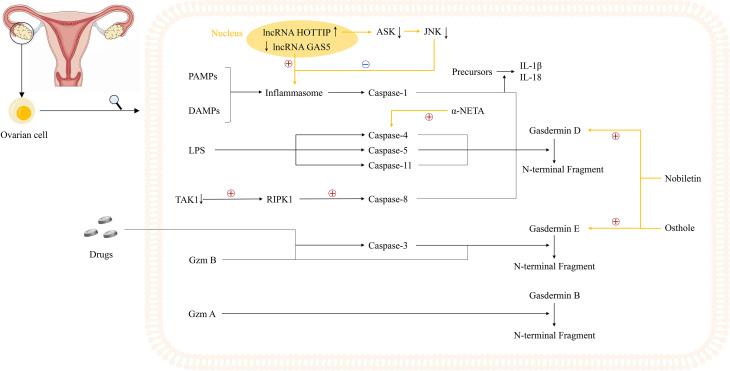
Figure 2.
Potential mechanisms underlying pyroptosis in ovarian cancer cells and current study foundations. Notably, two lncRNAs, GAS5 and HOTTIP, play an important role in the regulation of inflammasomes. The inhibited expression of lncRNA GAS5 in ovarian cancer could trigger the formation of inflammasome while lncRNA HOTTIP is highly expressed in ovarian cancer, the knockdown of which leads to upregulation of ASK1/JNK signaling, elevated formation of NLRP1-inflammasome, and pyroptosis. Moreover, three novel small molecules including osthole, nobiletin, and α-NETA are reported to regulate the pyroptosis process in ovarian cancer cells. Osthole and nobiletin are of high similarity since they both have an effect on ROS production, MMP, and LC3-related autophagy. However, osthole could mediate GSDME-dependent pyroptosis while nobiletin could mediate pyroptosis through GSDMD- and GSDME-dependent ways. Moreover, α-NETA treatment causes epithelial ovarian cancer cell death through pyroptosis, with dramatically augmented level of GSDMD and caspase-4.