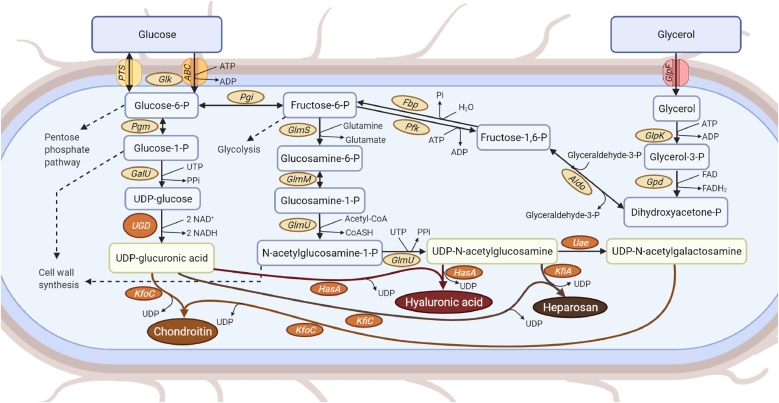
Fig. 3.
Production of glycosaminoglycans in microbes and its possible use in the biosynthesis of microbial chondroitin, hyaluronic acid or heparosan. Depending on the microbial host, the heterologous expression of the enzymes shown in orange boxes might be required for glycosaminoglycans production. Enzyme abbreviations: ABC, adenosine triphosphate (ATP)-binding cassette transporters; Aldo, fructose-6-phosphate aldolase; Fbp, fructose-1, 6-bisphosphatase; GalU, uridine triphosphate:glucose-1-phosphate uridylyltransferase; Glk, glucokinase; GlmM, phosphoglucosamine mutase; GlmS, glucosamine-6-phosphate synthase; GlmU, glucosamine-1-phosphate N-acetyltransferase/N-acetylglucosamine-1-phosphate uridyltransferase; GlpF, Glycerol uptake facilitator protein; GlpK, glycerol kinase; Gpd, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; HasA, hyaluronan synthase; KfiA, β−1, 3-glucuronyltransferase; KfiC, α−1, 4-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase; KfoC, chondroitin synthase; Pfk, 6-phosphofructokinase; Pgi, glucose-6-phosphate isomerase; Pgm, phosphoglucomutase; PTS, phosphotransferase system; Uae, UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 4-epimerase; UGD, uridine diphosphate (UDP)-glucose 6-dehydrogenase.