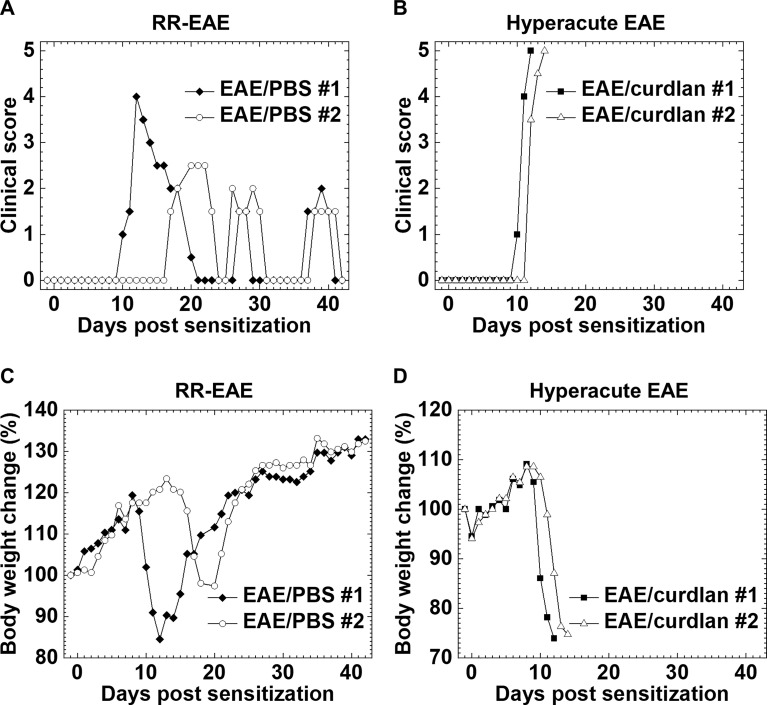
Figure 1.
Two clinical courses of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) induced with myelin proteolipid protein (PLP)139-151. One day prior to EAE induction, SJL/J mice were injected intraperitoneally (i.p.) with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) (EAE/PBS, A, C) or curdlan (EAE/curdlan, B, D). Mice were observed for clinical signs (A, B) and weight changes (C, D) for 6 weeks. In the EAE/PBS group, mice developed relapsing-remitting (RR)-EAE; the mice had hind limb paralysis around 2 weeks post sensitization, recovered within 10 days (remission), and had relapses once or twice during the 6-week observation period. In the EAE/curdlan group, mice develop hyperacute EAE; the mice had progressive motor paralysis without remission and died within 1 week following the disease onset. Results are the two representative mice of 12 mice per group from three independent experiments.