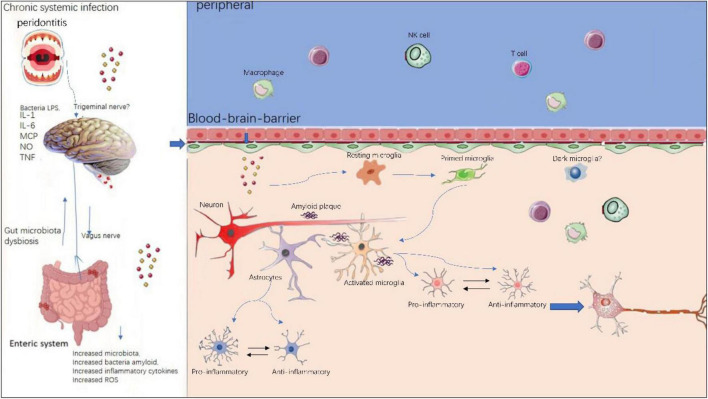
FIGURE 3.
Peripheral and central immune system crosstalk in AD. Chronic systemic infections such as periodontitis and gut microbiota dysbiosis will produce local infection and increased inflammatory cytokines and peripheral immune cells such as peripheral microphages and T cells, NK cells are able to enter the compromised blood–brain-barrier and exacerbate existing neuroinflammation in central nervous system. Within the brain, resident microglia transform from resting state to activated state upon stimulation. Initially, microglia and astrocytes exhibit anti-inflammatory phenotypes, however, sustained chronic inflammation will drive them toward pro- inflammatory phenotypes.