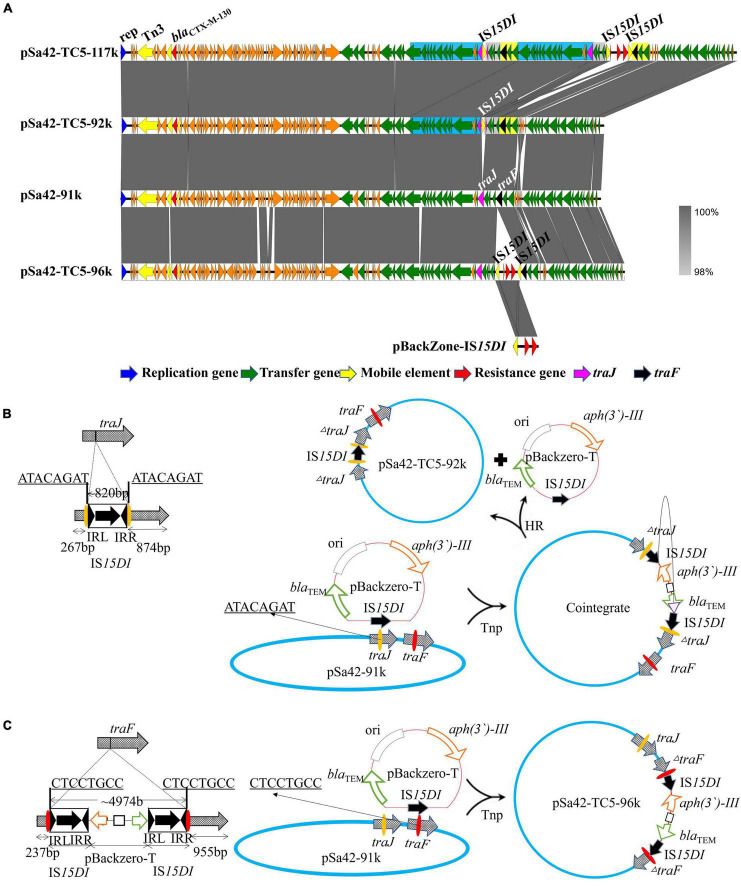
FIGURE 4.
Alignment of three plasmids in transconjugant Sa42-TC5 and schematic representation of the two insertion events. (A) Alignment of various plasmids harbored by strain Sa42-TC5. Plasmids pSa42-TC5-117k, pSa42-TC5-92k, and pSa42-TC5-96k were obtained from transconjugant Sa42-TC5; pSa42-TC5-117k had two target site duplications (TSD) and was assembled de novo with Canu, the slight blue, gray, and yellow color depicted various repeated regions. Plasmids pSa42-TC5-92k and pSa42-TC5-96k with one TSD were selected directly from nanopore long reads and calibrated by matching with known plasmid sequences. (B) Genetic mechanisms of insertion of IS15DI into traJ. IS15DI led to an attack on the hot spot in the traJ gene. Resolution of traJ via transposase (Tnp) mediated cointegration, which was followed by homologous recombination (HR). (C) Proposed IS element-mediated fusion in traF only via replicative transposition event at the hot spot (CTCCGTCC). Target site duplications from different genes were underlined with bold letters. The left and right inverted repeats 14 bp (IRL and IRR) of IS15DI were shown in black triangles. IS15DI was denoted in black with an arrow indicating the orientation and length of the transposase gene.