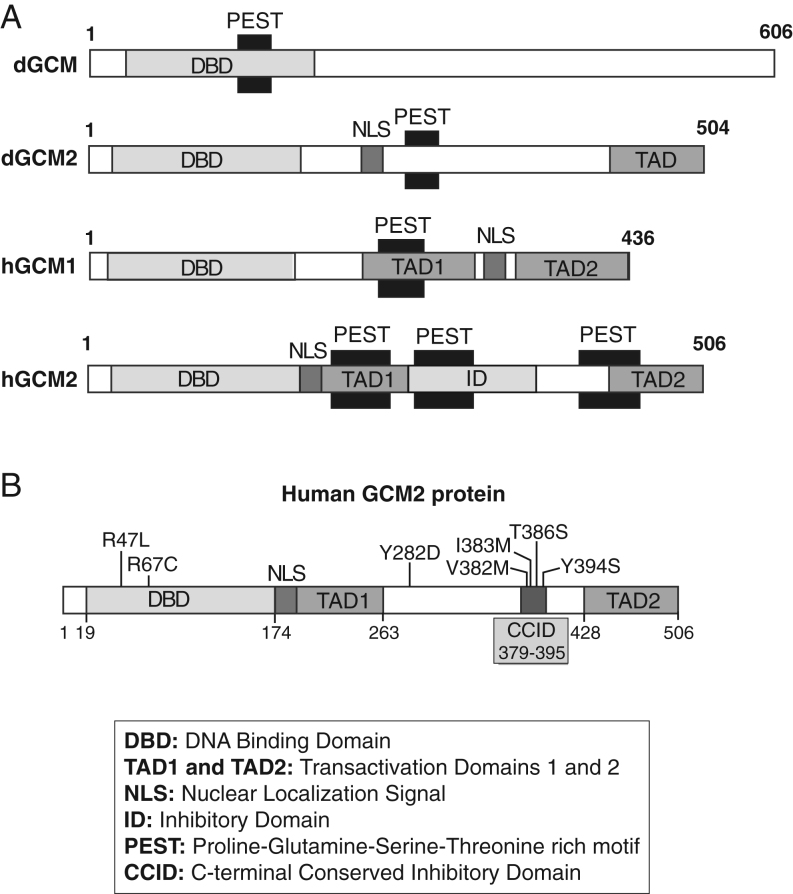
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of GCM protein domains and position of mutations/variants on human GCM2. (A) Protein structures of Drosophila and human GCM proteins are shown. All proteins possess a DNA-binding domain (DBD), nuclear localization signal (NLS), one or two transactivating domain 67 (TAD) and proline (P), glutamic acid (E), serine (S), and threonine (T)-rich (PEST) domain(s) implicated in rapid protein turnover. Human GCM2 contains an inhibitory domain (ID) and a unique C-terminal conserved inhibitory domain (CCID) (B). Positions of missense mutations in human GCM2 are shown. Germline mutations associated with hypoparathyroidism, and within the DBD, R67C (novel) and previously identify R47L (18). Germline mutations/variants associated with hyperparathyroidism, Y282D (32) and within the CCID, V382M, I383M, T386S and Y394S (14; present publication) are shown.

 This work is licensed under a
This work is licensed under a