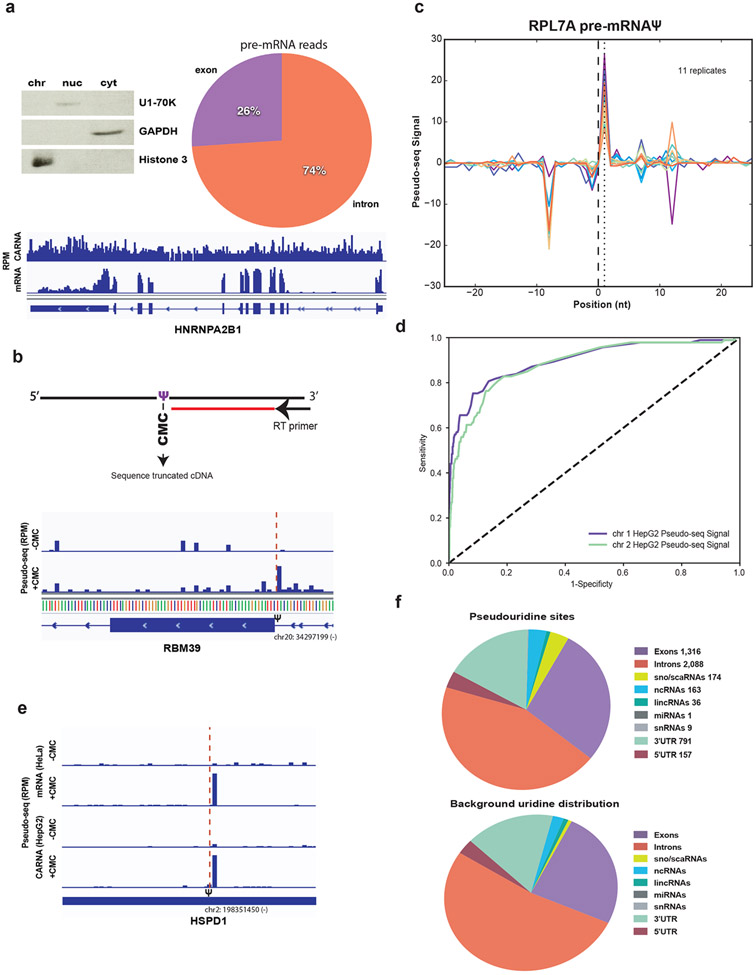
Figure 1. Pre-mRNA is pseudouridylated co-transcriptionally in human cells.
a) Left panel. Western blot of HepG2 cellular fractions, equal cell volumes were loaded and probed with antibodies against GAPDH (cytoplasm), U1-70K (nucleoplasm) and Histone3 (chromatin). Right panel. Distribution of pre-mRNA reads mapping to introns versus exons in the chromatin-associated RNA fraction. Bottom panel. Genome browser view of reads per million mapping across the highly expressed gene hnRNPA2B1 in a chromatin-associated RNA library compared to a poly(A)+ mRNA library from HepG2 cells. b) Detection of pseudouridine by Pseudo-seq with a representative genome browser view of Pseudo-seq reads mapping to RBM39, red dotted line indicates the location of the pseudouridine (chr20:34297199) identified by a CMC-dependent reverse transcriptase stop one nucleotide 3′ to the site. Reads per million (RPM). c) Pseudo-seq signal, equal to the difference in normalized reads between the +CMC and mock libraries. Traces for 11 biological replicates of chromatin-associated RPL7A pre-mRNA pseudouridine (chr9:136217792) are shown, d) ROC curve of true positive versus false positive rates of known pseudouridine locations in mature human rRNA for two representative chromatin-associated RNA replicates. The Pseudo-seq signal is displayed for both replicates, e) Representative genome browser view of Pseudo-seq reads mapping to HSPD1 from HepG2 chromatin-associated RNA and HeLa mRNA red dotted line indicates the location of this cell type conserved pseudouridine identified by a CMC-dependent reverse transcriptase stop one nucleotide 3′ to the site. f) Top panel. Summary of pseudouridines sites identified in chromatin associated RNAs. Bottom panel. Distribution of background uridines meeting the minimum read cutoff for site calling.