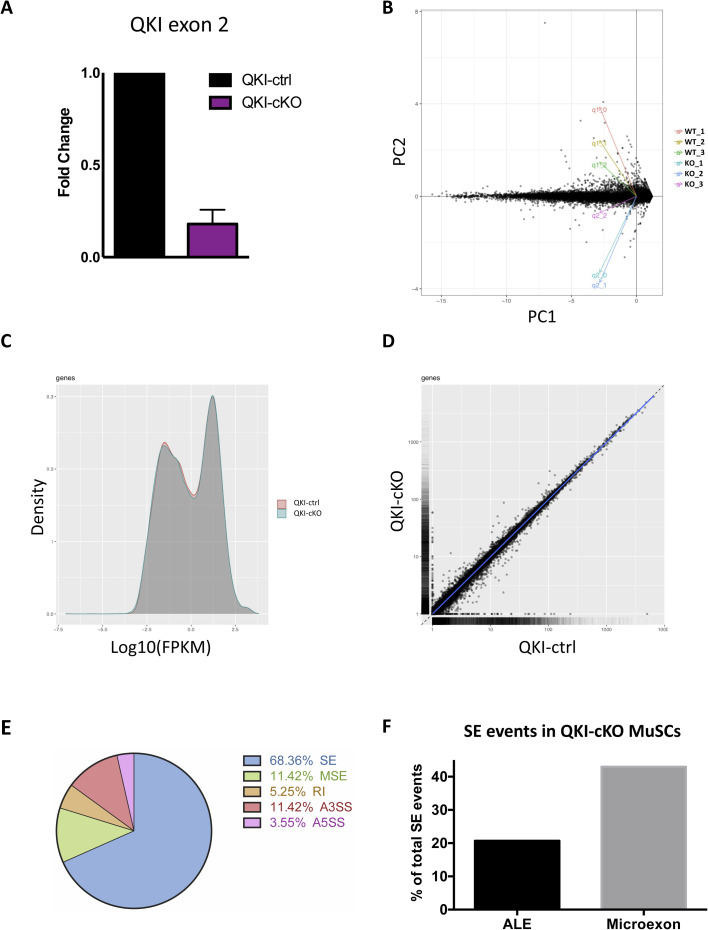
Figure S2.
QKI-deficient primary skeletal MuSCs drastically down-regulate markers of terminal differentiation. (A) RT-qPCR confirmation of QKI knockout in muscle stem cells used for RNA-seq (n = 3 biological replicates normalized to Gapdh levels, P = 0.0065 unpaired t test). (B) PCA plot of individual replicates. Dimensionality reduction was performed with cummeRbund software using Cufflinks output. (C) Distribution of FPKM scores across QKI-cKO and QKI-ctrl conditions from one replicate performed using cummeRbund software. (D) Pairwise scatterplot of gene expression from QKI-cKO and QKI-ctrl conditions. (E) Pie chart representing the summary of alternative splicing events in QKI-cKO muscle stem cells compared to QKI-ctrl (SE, skipped exon; MSE, multiple skipped exons; RI, retained intron; A3SS, alternative 3′ splice site; A5SS, alternative 5′ splice site). (F) Percentage of SE events which contained alternative last exon or microexons.