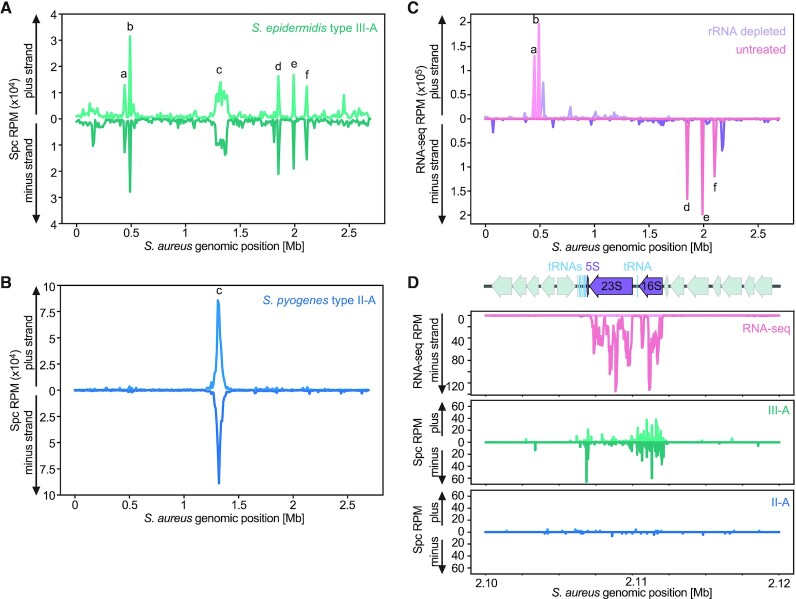
Figure 2.
Spacer acquisition by the S. epidermidis type III-A CRISPR-Cas system preferentially occurs at the chromosome terminus, rRNA loci and tRNA clusters. (A) Abundance (in reads per million, RPM) of spacers acquired 3 h after induction of the S. epidermidis type III-A acquisition machinery, mapped to the bacterial chromosome (10 kb bins). Peak labeled ‘c’ corresponds to the dif site, peaks labeled ‘a’, ‘b’, ’d’, ‘e’, ‘f’ correspond to the five rRNA loci in the S. aureus genome. (B) Abundance (RPM) of spacer acquired 3 h post induction of the S. pyogenes type II-A acquisition machinery, mapped to the bacterial chromosome (10 kb bins). Peak labeled ‘c’ corresponds to the dif site. (C) Abundance (RPM) of S. aureus RN4220 RNA-seq reads, of either an rRNA depleted sample (purple) or an untreated sample (pink), mapped to the bacterial chromosome (10 kb bins). Peaks labeled ‘a’, ‘b’, ’d’, ‘e’, ‘f’ correspond to the five rRNA loci in the S. aureus genome. (D) Details of the RNA-seq (rRNA depleted sample, purple; untreated sample, pink), type III-A (green) and type II-A (blue) spacer acquisition data (RPM), obtained 3 h post-induction, for the ribosomal RNA locus rrnE (peak ‘f’ in (B)) of S. aureus RN4220.