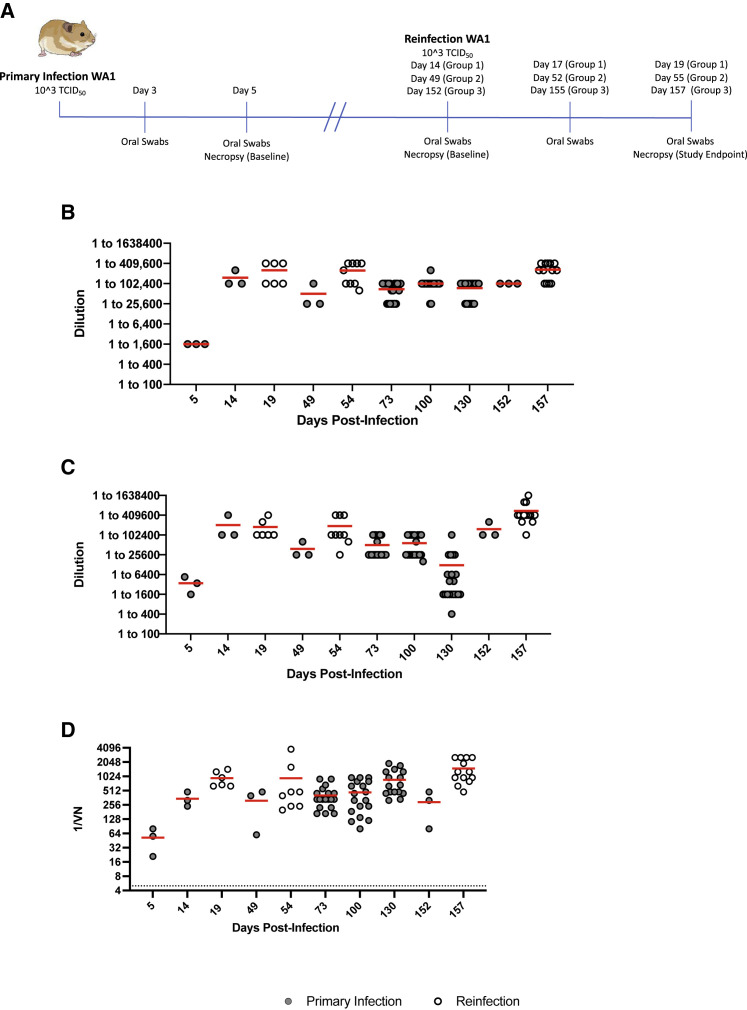
Figure 2.
Design of homologous reinfection study and humoral immune response to infection and reinfection
(A) Homologous reinfection study. Hamsters (n = 40) were infected intranasally with 1 × 103 TCID50 of WA1 SARS-CoV-2 and swabbed at 3 DPI and 5 DPI to monitor shedding and ensure all animals were infected. Three animals were randomly selected and necropsied at 5 DPI to measure disease and infectious titers in the lung. The remaining 37 animals were divided into 3 groups for reinfection at varying timepoints. Groups 1 (n = 9), 2 (n = 12), and 3 (n = 16) were allowed to recover for 14, 49, and 152 DPI after primary infection and were reinfected with WA1 SARS-CoV-2. Three animals from each group were euthanized before reinfection as infection controls for viral replication and pathology (baseline). The humoral response was measured over the course of the study with serum collected at terminal timepoints; additionally serum was collected from group 3 at 73, 100, and 130 DPI. Oral swabs were collected at 3 DPR and 5 DPR to monitor viral shedding. Lung tissue was collected from all control and reinfected hamsters at the time of necropsy (5 DPR) to determine viral titers and lung pathology.
(B) Total IgG antibodies against the spike protein. Total IgG antibodies were determined using an in-house ELISA dilution series assay targeting the S1 region of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein.
(C) Total IgG antibodies against the RBD. Total IgG antibodies were determined using an in-house ELISA assay targeting the RBD of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein.
(D) Neutralizing antibodies. Neutralizing antibody titers were determined through a TCID50-based neutralization assay using two-fold serially diluted hamster serum and the homologous SARS-CoV-2 WA1-2020 strain. Solid gray circles are data points from singly infected and hollow white circles are data points generated from reinfected animals. Statistical differences were determined using nonparametric one-way AVOVA (Kruskal-Wallis) with correction for multiple comparisons.