Table 1.
Summary of VEA vaping emission production yields.
| Name | Formula | M.W.a | B.P.b | Estimated vapor pressurec |
Structure | EIC (m/z)d |
Production Yielde |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vitamin E acetate(VEA) | C31H52O3 | 472.7 | 485 | 4.03 × 10−8 |
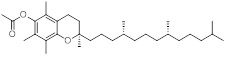
|
472 | (1.68 ± 0.09) ×10−1 |
| Vitamin E | C29H50O2 | 430.7 | 486 | 1.35 × 10−8 |
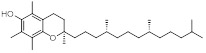
|
205 | (2.21 ± 0.01) ×10−2 |
| 1-Pristene | C19H38 | 266.5 | 290 | 5.8 × 10 −3 |
|
126 | (1.07 ± 0.07) ×10−2 |
| 3,7,11-Trimethyl-1-dodecanol | C15H32O | 228.4 | 279 | 2.11 × 10−4 |
|
111 | (3.44 ± 0.20) × 10−4 |
| Durohydroquinone (DHQ) | C10H14O2 | 166.2 | 312 | 1.77 × 10−6 |
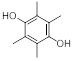
|
166 | (2.20 ± 0.13) × 10−4 |
| Duroquinone (DQ) | C10H12O2 | 164.2 | 230 | 1.26 × 10−3 |
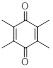
|
121 | (7.70 ± 0.28) × 10−5 |
M.W.: molecular weight (g mol−1)
B.P.: boiling point (°C) at 1 atm
Estimated vapor pressure: mmHg at 25 °C
Extracted ion chromatogram (EIC); ion selected for quantification
mg-Product recovered mg-VEA comsumed−1
Six major emission products were quantified using authentic or surrogate standards.
