Figure 1. Seizures exhibit different patterns at termination.
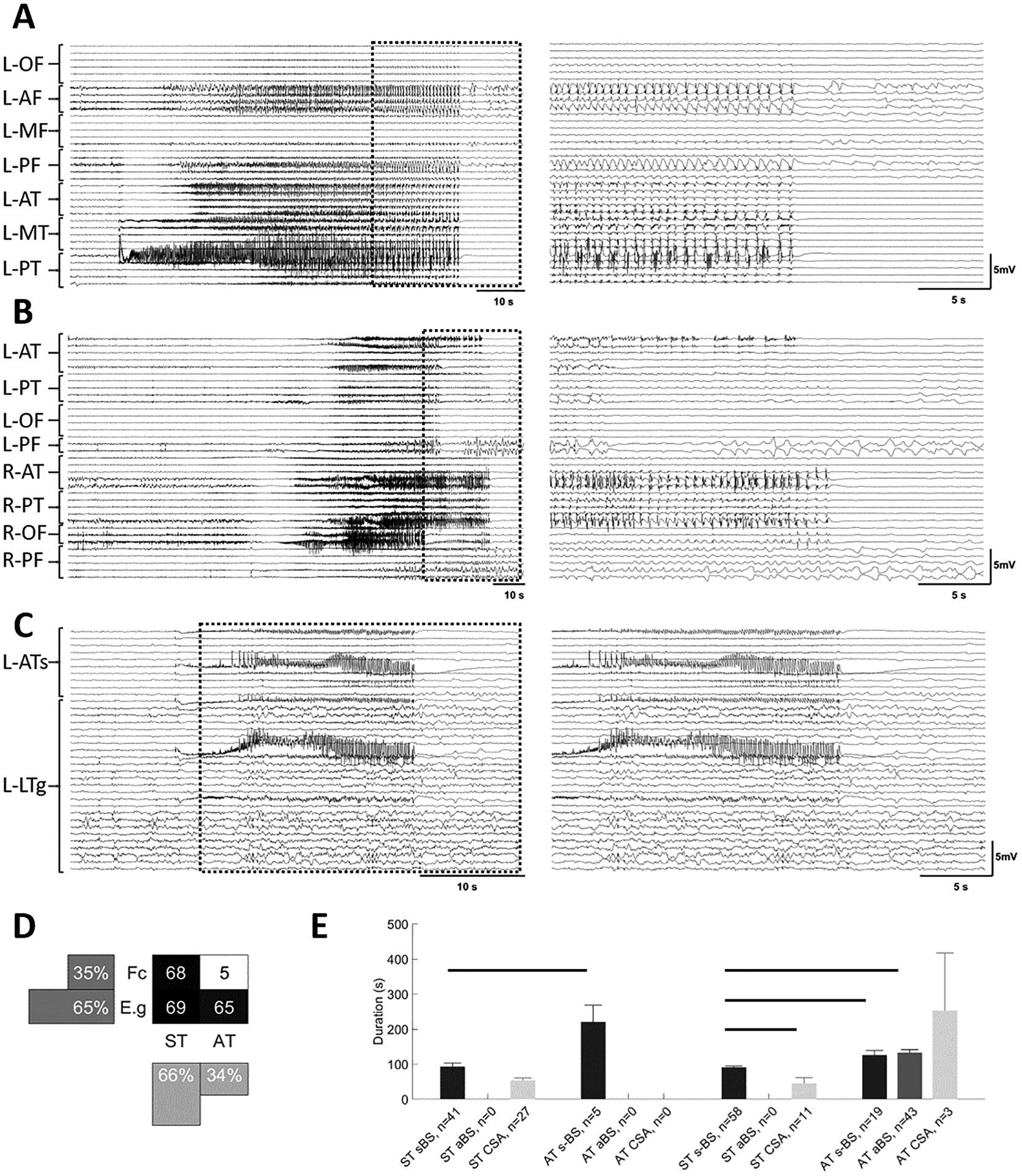
Examples of seizures with different focality and termination patterns. Seizure traces from 10 s before the onset until 10 s after their termination (A-C, left panels). An expanded view of these traces (A-C, right panels) shows the last 20 s of each seizure and the 10 s post termination period. This 30 s period is identified on the left with dashed boxes. A) Seizure with onset in left posterior temporal area with synchronous termination (ST). In the right panel, note the burst suppression activity before the termination. B) Seizure with onset in right anterior temporal area that propagates to the rest of the brain, terminating in some channels while continuing in others (AT). C) Seizure that starts focally in left anterior temporal area and remains focal for the duration of the seizure with synchronous termination (ST) with bursting activity at termination. Seizures in each group were further classified into three subgroups: seizures with synchronous burst and suppression activity across almost all channels at the end of the seizure (sBS, A), and seizures that show burst and suppression activity before seizure termination in most channels, but with burst suppression activity not synchronized across all channels (aBS, B), seizures with continuous seizure activity patterns (CSA, C). D) A distribution of seizures based on focality and the termination pattern (ST and AT). E) The duration of seizures in different groups. In both focal and electrographic generalization groups, CSA seizure had significantly shorter duration compared to sBS seizures. Horizontal bars indicate significance between the pairs (p<0.05). L: left; R: right; OF: orbitofrontal; AF: anterior frontal; MF: middle frontal; PF: posterior frontal; AT: anterior temporal; MT: middle temporal; PT: posterior temporal; ATs: anterior temporal strip; LTg: lateral temporal grid; Fc: focal; E.g: electrographic generalization.
