Figure 4.
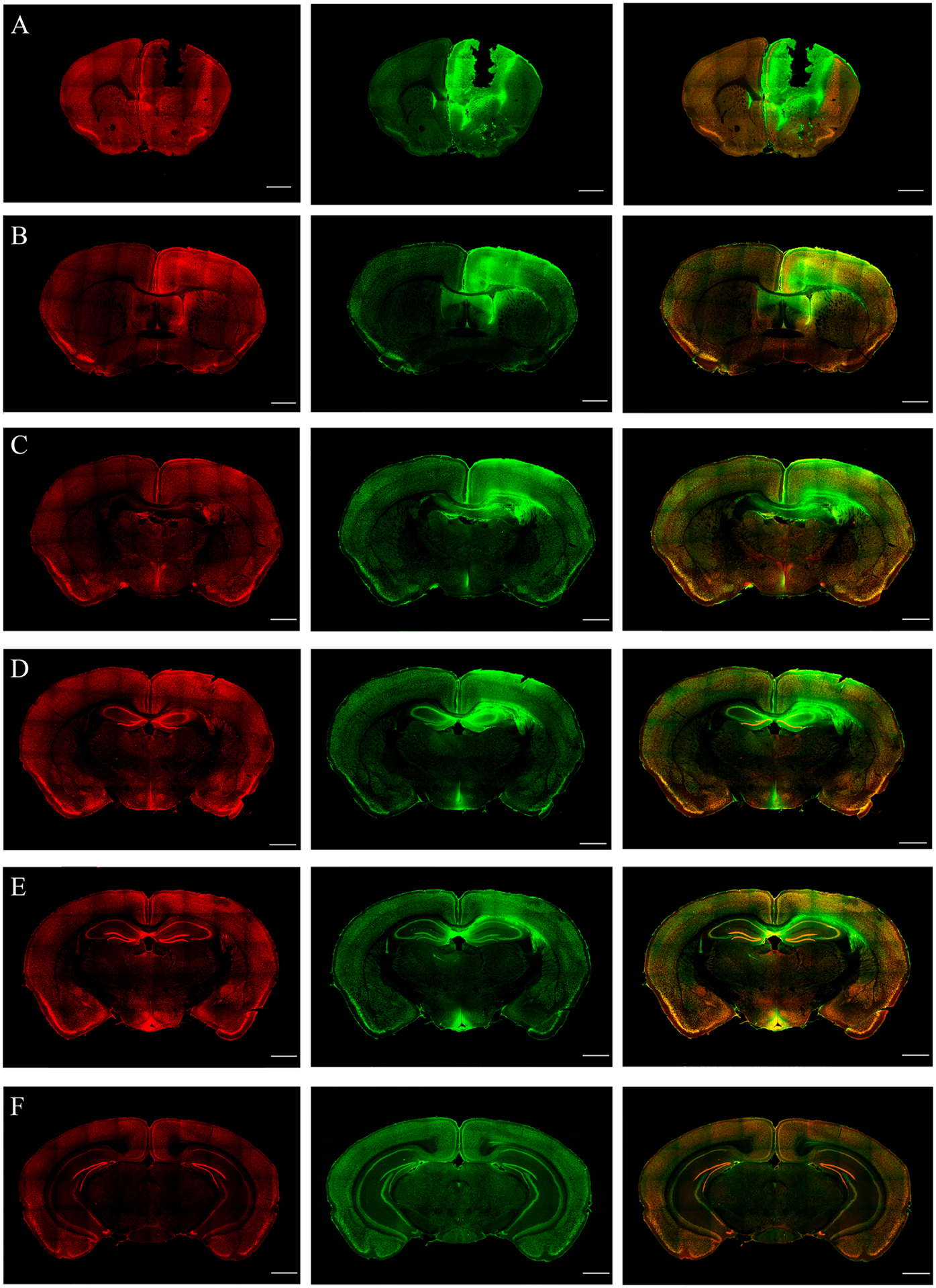
cFos immunoreactivity (IR) in the different brain regions during continuous generalized convulsive seizures are shown using the coronal sections at the level of bregma 1.5, 1.0, −0.5, −1.0, −2.0, −3.0 mm (A to F, respectively; scale bar =1000 μm). (A-B) Coronal sections at the level of bregma 1.5 and 1.0 mm (A and B, respectively) show the Co lesion and cFos immunoreactivity in the cortical and subcortical areas, such as the motor cortex, somatosensory cortex, septal nucleus and anterior cingulate gyrus. The activation is found to be bilateral. (C-D) Coronal sections at the level of bregma −0.5 and −1.0 mm (C and D, respectively) indicating the bilateral activation of cortical, amygdalar, and thalamic nuclei. (E-F) Coronal sections at the level of bregma −2.0 and −3.0 mm (E and F, respectively), indicating bilateral cFos IR in various cortical regions, such as the posterior-parietal association area, primary somatosensory area and auditory area, Please note that intense cFos IR was observed at the hippocampus.
