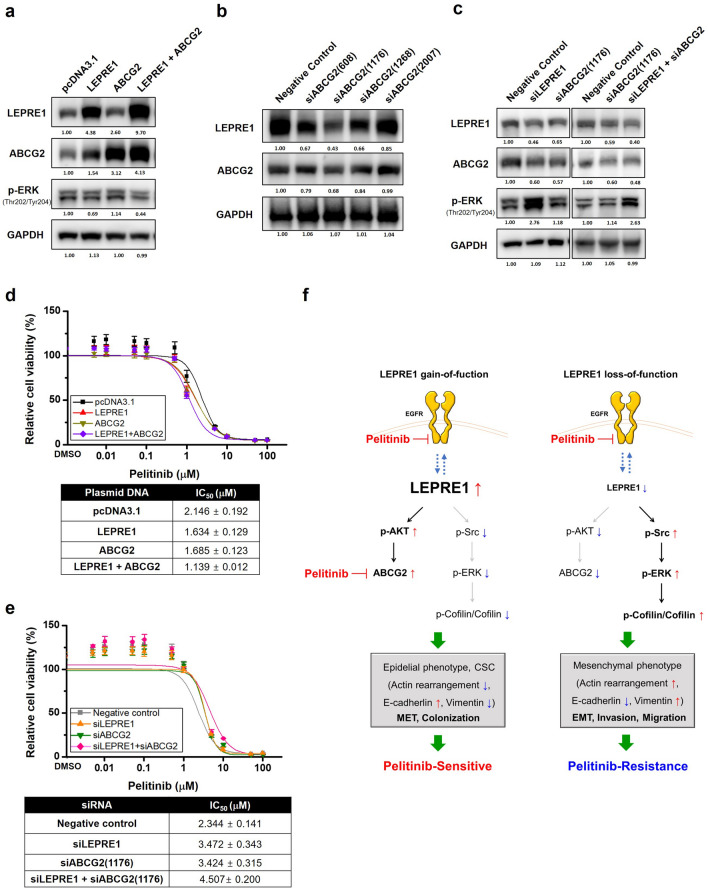
Figure 7.
Proposed mechanism of action for LEPRE1 in pelitinib-sensitive or pelitinib-resistant A549 cells. (a) Western blot analysis of LEPRE1, ABCG2 and, p-ERK expression after overexpression or co-transfection of LEPRE1 and ABCG2 in the A549 cell lien. (b) Protein expression levels of ABCG2 determined following A549 cells being transfected with ABCG2-si608, -si1176, -si1268, -si2007, or negative control siRNA. (c) Western blot analysis of LEPRE1, ABCG2, and p-ERK expression after siRNA single or co-transfection of siLEPRE1 and siABCG2 in A549 cells. All western blots are pre-cut. Membranes were often stripped and reprobed for multiple antibodies. (d,e) LEPRE1-, ABCG2-overexpression or co-transfection (d) or LEPRE1, ABCG2 knockdown or double knockdown (e) A549 cells were treated with pelitinib for 3 days. Cell viability was determined using a WST-1 proliferation assay. (f) ABCG2 Schematic model showing that overexpression of LEPRE1 induces AKT activation and ABCG2 overexpression, which results in increased E-cadherins levels and a colonization phenotype, ultimately leading to changes resulting in sensitivity to pelitinib. Meanwhile, silencing of LEPRE1 results in activation of the Src/ERK/Cofilin signaling pathway, which leads to increased vimentin levels and the acquisition of an EMT-like phenotype. This ultimately leads to changes resulting in resistance to pelitinib.