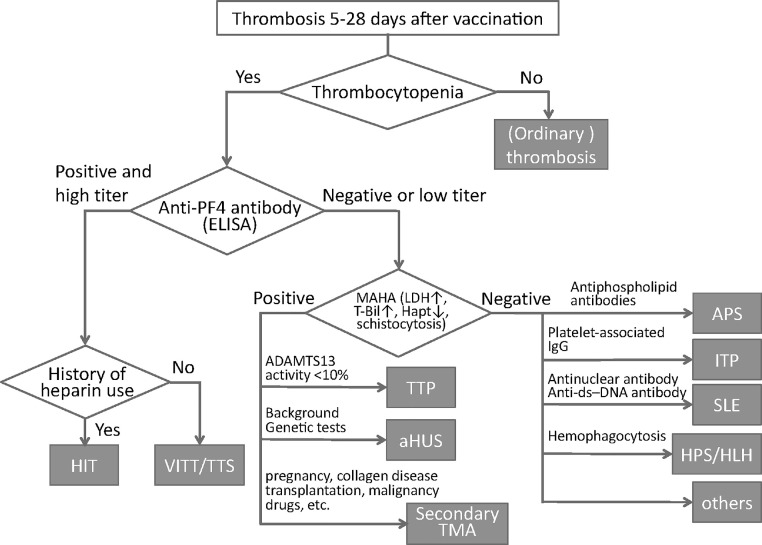
Fig. 2.
Algorithm to differentiate vaccine-induced thrombotic thrombocytopenia (VITT)/thrombosis with thrombocytopenia syndrome (TTS) from other thrombotic diseases. When the patients show thrombosis between 5 and 28 days after COVID-19 vaccination, the platelet count should be calculated. If patients show low platelet count, vaccine-induced thrombocytopenia (VITT)/thrombosis with thrombocytopenia syndrome (TTS) should be differentiated from other thrombotic diseases by measuring antiplatelet factor 4 (PF4) antibody. Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) is suspected when the patients have a history of heparins. If anti-PF4 antibody is negative or low titer, the presence of microangiopathic hemolytic anemia (MAHA) should be examined by measuring lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), total-bilirubin (T-Bil), haptoglobin (Hapt). TTP: thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura, aHUS: atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome, TMA: thrombotic microangiopathy, APS: antiphospholipid syndrome. ITP: immune thrombocytopenic purpura, ds-DNA: double strand-DNA, SLE: systemic lupus erythematosus, HPS: hemophagocytic syndrome, HLH: hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis.