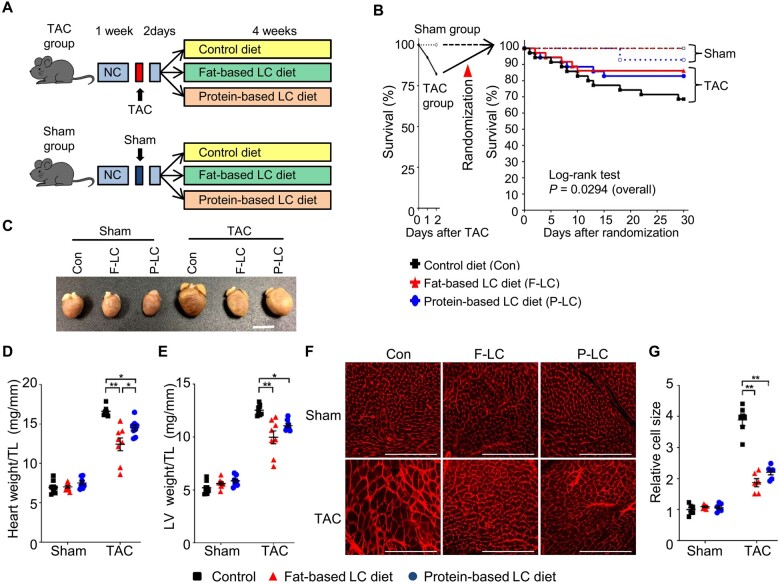
Figure 1.
LC diets attenuate pressure overload-induced cardiac hypertrophy. (A) Schematic representation of the study design. After a 1-week running period of NC, 8- to 10-week-old C57BL/6J wild-type (WT) mice were subjected to TAC or sham operation, followed by a 2-day observation period with NC. The surviving mice were randomly assigned to three groups: LC diet supplemented with high fats, LC diet supplemented with high proteins, or isocaloric high-carbohydrates control diet. (B) Kaplan–Meier survival curves after TAC or sham surgery. Overall statistical differences after the surgeries were analysed by log-rank test (n = 14 for sham and n = 35–36 for TAC groups). (C–G) The mouse hearts were harvested 4 weeks after the randomization into the indicated diet. (C) Representative gross appearance of the indicated hearts. Scale bar, 5 mm. (D) Heart weight normalized by tibial length (TL) (n = 7–8). (E) LV weight normalized by TL (n = 7–8). (F) Representative WGA staining. Scale bar, 200 μm. (G) Quantification of relative cardiomyocyte size (n = 6). One-way ANOVA followed by the Tukey’s post hoc analysis was used. Error bars indicate SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.001.