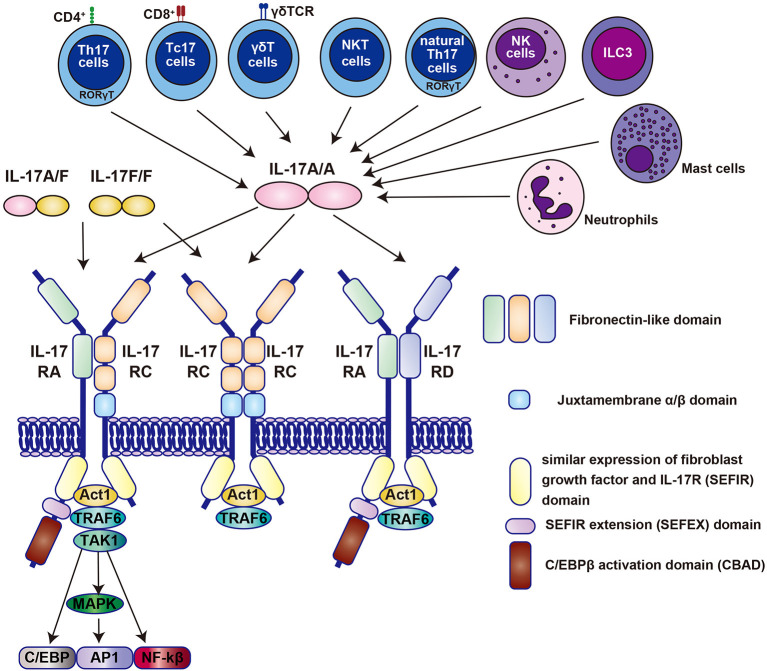
Figure 1.
The molecular binding system of the IL-17 family centered on IL-17A and its receptors. All the family members of the IL-17 family, except IL-17D function as homodimer, whereas IL-17A and IL-17F form a heterodimer (denoted as IL-17A/F) (21). All receptors also function as homodimers or heterodimers. Homodimers of IL-17A (denoted as IL-17A/A) selectively bind to specific IL-17RA/RC, RC/RC, or RA/RD receptor complexes. Contrastingly, IL-17A/F and IL-17F/F bind only to IL-17RA/RC and RC/RC receptor complexes. Each IL-17 receptor has an extracellular fibronectin-like domain that binds the ligand and an intracellular SEFIR (similar expression of fibroblast growth factor and IL-17R) domain that recruits molecules such as Act1 and TRAF6 (21). The IL-17 receptor family has been shown by Goepfert et al., to be structurally bent between the first and second fibronectin domains (22). IL, interleukin; Th17, T helper 17; Tc17, IL-17-producing CD8+ T cells; NKT, natural killer T cells; NK; natural killer cells; ILC3, type 3 innate lymphoid cells; NF, nuclear factor; TRAF6, tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; TAK1; transforming growth factor-β-activated kinase 1.