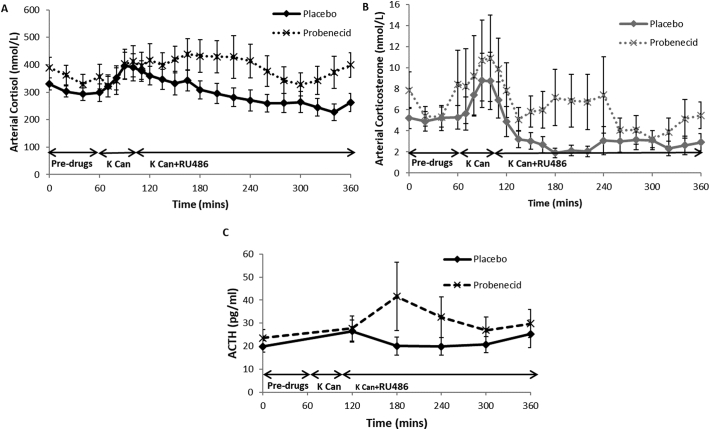
Fig. 2.
Effect of ABCC1 inhibition on whole body cortisol, corticosterone and ACTH concentrations during MR +/− GR antagonism. Data are mean ± SEM for plasma cortisol (A) and corticosterone (B) concentrations in arterialised samples at time points 0–360 min during placebo (unbroken lines) and probenecid phases (dashed lines) (n = 14). Potassium canrenoate (K Can) and mifepristone (RU486) increased cortisol concentrations (p < 0.001) and probenecid significantly increased cortisol compared to placebo (p = 0.05). K Can and RU486 increased corticosterone concentrations (p < 0.001) while probenecid tended to increase corticosterone (p = 0.08). (C) Plasma ACTH concentrations in placebo (black unbroken line) and probenecid phases (black dashed line) (n = 14). Probenecid tended to increase ACTH (p = 0.05).