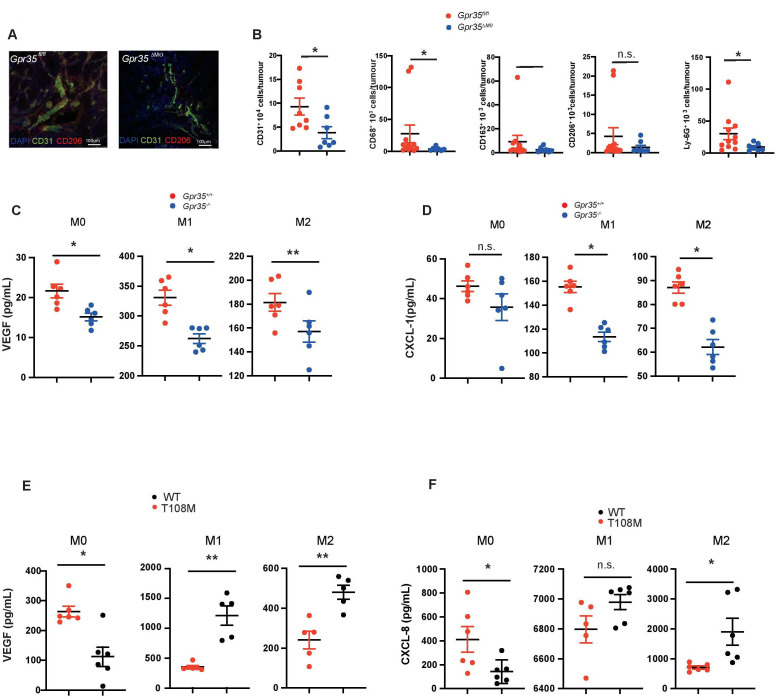
Figure 2.
GPR35 deletion in myeloid cells reduces angiogenic potential. (A) Adenomas from Gpr35fl/fl and Gpr35 ΔMΦ mice exposed to AOM/DSS stained for CD31+ endothelial cells and CD206+ M2 macrophages. N=5 each genotype, representative confocal microscopy. Scale bars 100 µm. (B) FACS analyses of CD31+, CD68+, CD163+, CD206+ and Ly-G6+ cells in Gpr35fl/fl and Gpr35 ΔMΦ tumour tissue. N=8–12 Gpr35fl/fl tumours from 8 to 12 mice and N=7 Gpr35 ΔMΦ tumours from mice. (C) VEGF levels in M0, M1 and M2 BMDM from Gpr35+/+ and Gpr35-/- mice. N=6 per genotype. (D) CXCL-1 levels in M0, M1 and M2 BMDM from Gpr35+/+ and Gpr35-/- mice. N=6 per genotype. (E) VEGF levels in supernatants of M0, M1 and M2 human iPS cell-derived macrophages. N=6 each genotype. (F) CXCL-8 levels in supernatants of M0, M1 and M2 human iPS cell-derived macrophages. N=6 each genotype. * p<0.05, ** p<0.01. AOM/DSS, azoxymethane followed by dextran sodium sulphate; iPS, inducible-pluripotent-stem; n.s., not significant; WT, wild type.