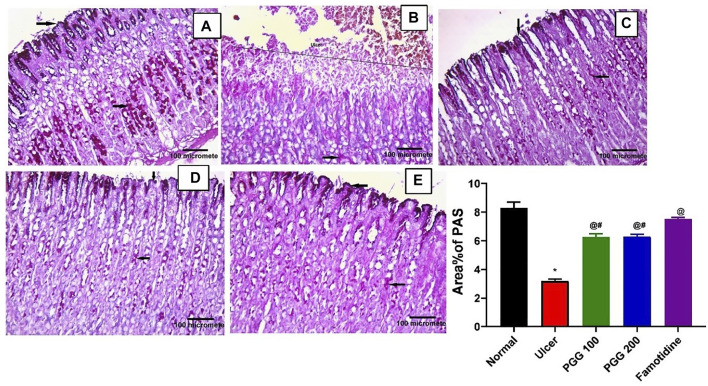
FIGURE 2.
Pentagalloyl glucose (PGG) effects on the gastric glycoprotein content of the gastric mucosa of ulcerative rats. Photomicrographs of gastric sections stained by Periodic acid–Schiff stain (PAS) collected from (A) normal control group, (B) ulcerative animals (indomethacin group, 60 mg/kg), (C,D) indomethacin + PGG-treated groups (100 mg/kg, and 200 mg/kg, respectively), and (E) indomethacin + famotidine-treated group (10 mg/kg). [PAS × 200]. The bar graph showed quantitative analysis of area percentage of PAS staining. Results are expressed as mean ± SEM, n = 10. *, @, #significantly different compared to the control group and indomethacin and famotidine groups, respectively at p < 0.05 by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test.