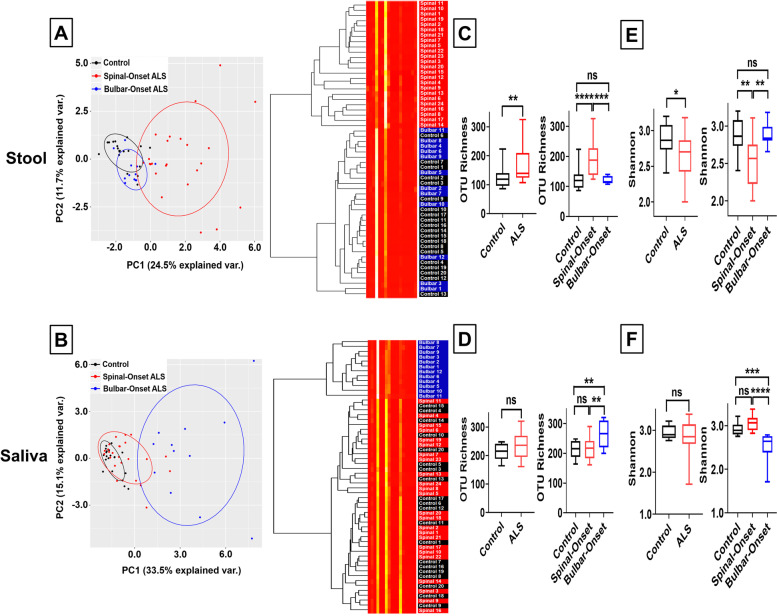
Fig. 2.
Spinal-Onset ALS Patients Manifest Gut-Dysbiosis, whereas Bulbar-Onset ALS Patients Display Oral-Dysbiosis. A Left panel represents principle component analysis of gut-microbiome species taxa at the phylum level. Right panel represents the heatmap for gut-microbiome distribution at the phylum level. Data derived from 20 healthy controls (black), 24 spinal-onset ALS patients (red), and 12 bulbar-onset ALS patients (blue). Spinal-onset ALS patients formed a distinct cluster from controls and bulbar-onset ALS patients. B Left panel represents principle component analysis of oral-microbiome species taxa at the phylum level. Right panel represents the heatmap for oral-microbiome distribution at the phylum level. Bulbar-onset ALS patients formed a distinct cluster from controls and spinal-onset ALS patients. C Gut-microbiome bacterial species number measured by Operational Taxonomic Unit (OTU) Richness. Results represent both ALS (spinal- and bulbar-onset ALS combined) or spinal- and bulbar-onset ALS quantified separately. Spinal-onset ALS patients displayed a significant increase in gut bacterial species count. No significant change in bulbar-onset ALS patients. D Oral-microbiome bacterial species number measured by OTU Richness. Bulbar-onset ALS patients displayed a significant increase in oral bacterial species count. No significant change in spinal-onset ALS patients. E Gut-microbiome species evenness measured through Shannon index. Spinal-onset ALS patients displayed a significant decrease in Shannon index, suggesting reduced gut-microbiome uniformity. No significant change in bulbar-onset ALS patients. F Oral-microbiome species evenness measured through Shannon index. Bulbar-onset ALS patients displayed a significant decrease in Shannon index, suggesting reduced oral-microbiome uniformity. No significant change in spinal-onset ALS patients. Statistics: For comparisons between controls and ALS patients (combined), Mann–Whitney test was utilized. For contrasts between control, spinal-onset ALS, and bulbar-onset ALS, Kruskal–Wallis test with Dunn’s post-hoc multiple comparisons test was utilized. Values represent sample median with interquartile range. Clustering was performed based on Bray Similarity matrix. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001