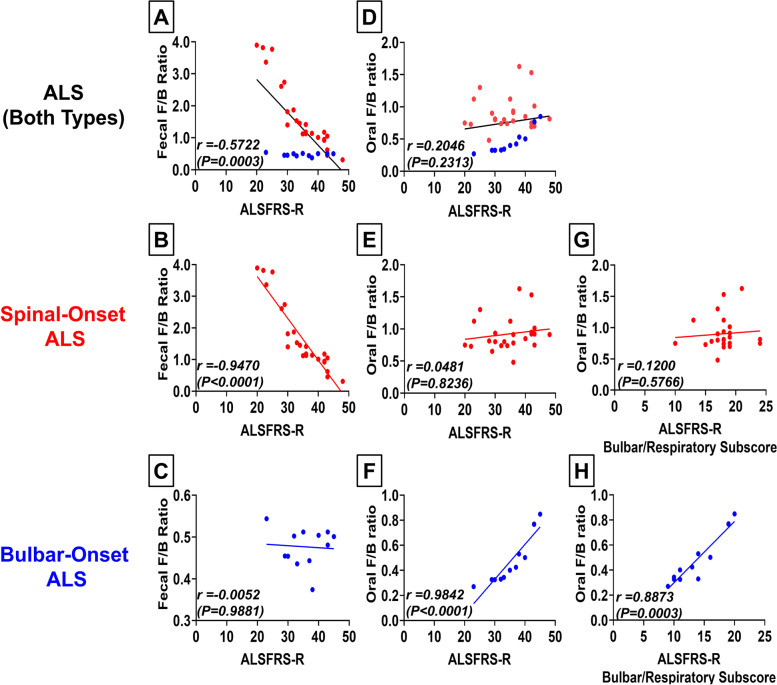
Fig. 5.
Gut-Dysbiosis Predicts Disease Severity of Spinal-Onset ALS, whereas Oral-Dysbiosis Predicts Disease Severity of Bulbar-Onset ALS. A Linear regression analysis comparing fecal F/B ratio and ALS severity score (ALSFRS-R) for all ALS patients combined. The ALSFRS-R gives a total of 48 points, and a lower ALSFRS-R score indicates greater motor impairment (0 = worst function; 48 = best function)[7]. Spinal-onset ALS patients shown in red, bulbar-onset ALS patients in blue. Higher fecal F/B ratio was strongly associated with lower ALSFRS-R score (greater ALS severity) with distinct patterns between the two ALS subtypes. B Linear regression analysis comparing fecal F/B ratio and ALSFRS-R score for spinal-onset ALS patients alone. In spinal-onset ALS patients, higher fecal F/B ratio was strongly associated with lower ALSFRS-R score (greater ALS severity). C Linear regression analysis comparing fecal F/B ratio and ALSFRS-R score for bulbar-onset ALS patients alone. Bulbar-onset ALS patients displayed no significant association between fecal F/B ratio and ALSFRS-R score/ALS severity. D Linear regression analysis comparing oral F/B ratio and ALSFRS-R score for all ALS patients combined. Spinal-onset ALS patients shown in red, bulbar-onset ALS patients in blue. We observed no overall trend for association between oral F/B ratio and ALSFRS-R score with distinct patterns between the two ALS subtypes. E Linear regression analysis comparing oral F/B ratio and ALSFRS-R score for spinal-onset ALS patients alone. Spinal-onset ALS patients displayed no significant association between oral F/B ratio and ALSFRS-R score/ALS severity. F Linear regression analysis comparing oral F/B ratio and ALSFRS-R score for bulbar-onset ALS patients alone. In bulbar-onset ALS patients, lower oral F/B ratio was strongly associated with lower ALSFRS-R score (greater ALS severity). G Linear regression analysis comparing oral F/B ratio and bulbar/respiratory ALSFRS-R subscore for spinal-onset ALS patients alone. Bulbar/respiratory ALSFRS-R subscore (maximum score of 24) measures the severity of bulbar/respiratory symptoms. Lower subscore indicates more severe bulbar/respiratory symptoms[7]. Spinal-onset ALS patients displayed no significant association between oral F/B ratio and bulbar/respiratory ALSFRS-R subscore. H Linear regression analysis comparing oral F/B ratio and bulbar/respiratory ALSFRS-R subscore for bulbar-onset ALS patients alone. In bulbar-onset ALS patients, lower oral F/B ratio was strongly associated with lower bulbar/respiratory ALSFRS-R subscore. Statistics: Statistical significance was established using linear regression analysis and Spearman’s correlation coefficient (r) test