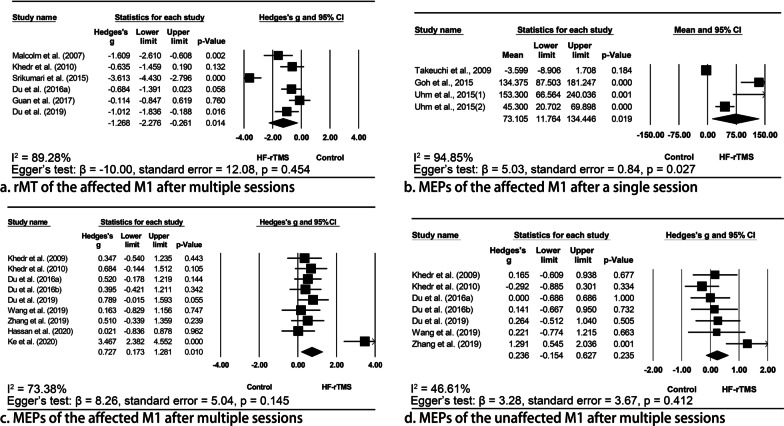
Fig. 3.
Meta-analyses indicating the effects of high frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (HF-rTMS) to the affected M1 in modulating bilateral cortical excitability. A meta-analysis indicated that multiple sessions of HF-rTMS applied to the affected M1 significantly decreased the rMT of the affected M1 (a). A single session of HF-rTMS significantly increases MEP amplitudes of the affected M1 by 73.11% (b). Multiple sessions of HF-rTMS also significantly increased MEP amplitudes of the affected M1 (c). However, multiple sessions of stimulation had no effects on the MEP amplitude of the unaffected M1 (d). rMT resting motor threshold, MEP motor-evoked potentials