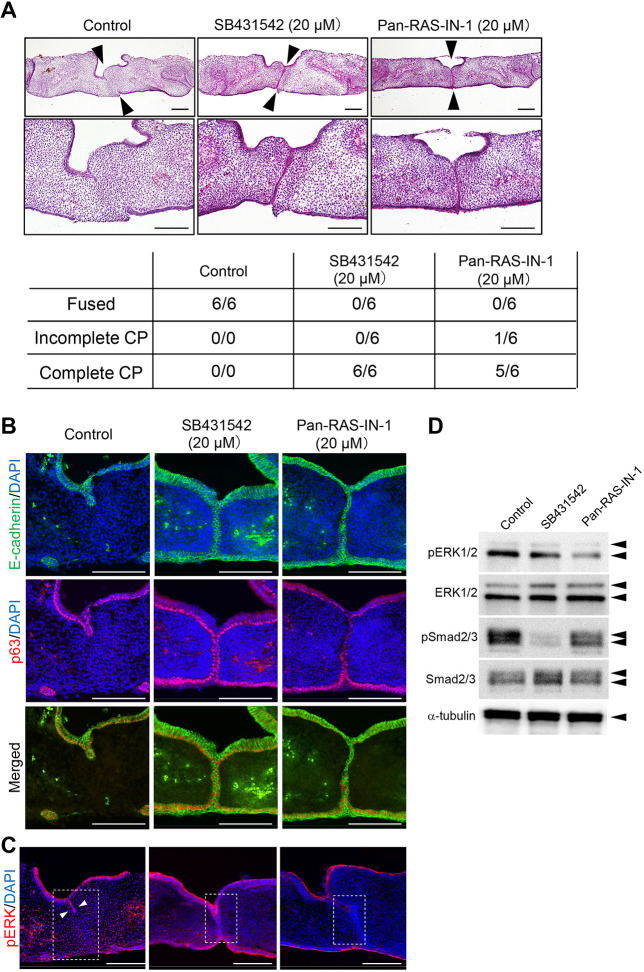
Fig. 1.
Pan-Ras inhibitor prevents palate fusion in organ culture. (A) Palatal shelf organ cultures were prepared using a pair of the dissected shelves from wild-type mice at E14.5, culturing for 48 h. Dissected shelves were pretreated with SB431542 (20 µM), Pan-Ras-IN-1 (20 µM) or dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) for 6 h prior to organ culture. Histological sections of horizontal palatal shelves showed the complete fusion defects of the palatal shelves and the remaining medial edge epithelium (MEE) in SB431542-treated and Pan-Ras-IN-1-treated groups. Arrowheads indicate the contact region of the paired shelves. The lower panel displays the incidence of palatal fusion in each treatment group. CP, cleft palate. (B) The persistent expression of E-cadherin and p63 was observed in the MEE region despite forced contact between the palatal shelves in the SB431542- and Pan-Ras-IN-1-treated groups. (C) The overall expression of phosphorylated (p)ERK is decreased in the Pan-Ras-IN-1-treated group. Note that positive expression was observed at the oral epithelial triangle region in the control culture (arrowheads). In contrast, the Pan-Ras-IN-1-treated cultures show substantially lower expression of pERK at the remaining MEE seam. (D) Western blotting confirmed the decreased expression of pERK in Pan-Ras-IN-1-treated cultures. The expression of pSmad2 is decreased by SB431542 treatment in cultured palatal shelves. Scale bars: 200 μm. The experiments in B, C and D were performed at least three times with similar results.