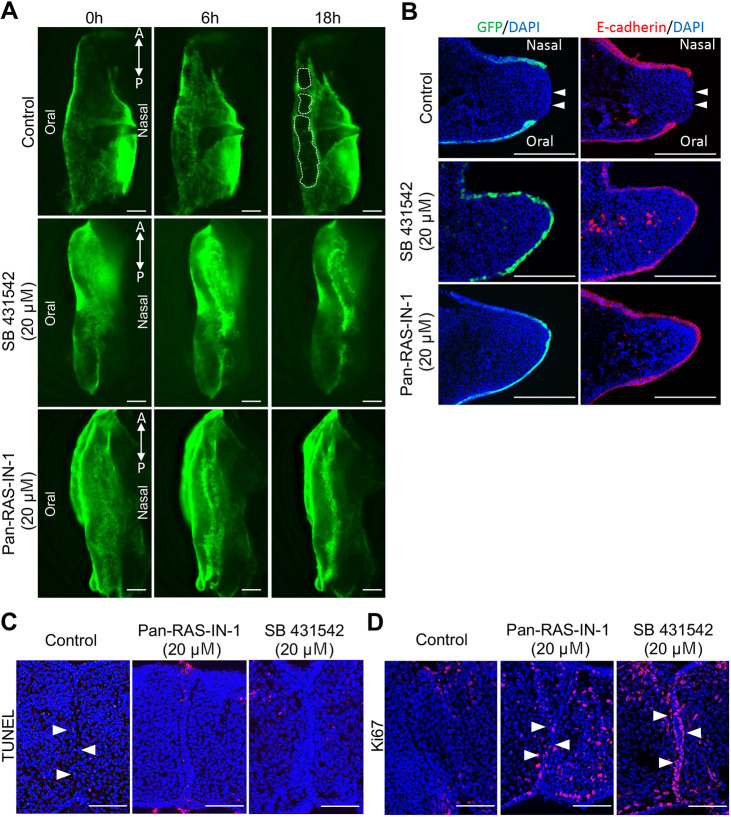
Fig. 2.
Pan-Ras inhibitor attenuates MEE cell migration and apoptosis in unpaired palatal explants. Epithelial behavior in the unpaired palatal explant model. (A) Fluorescence microscopic images showing the medial edges of the unpaired palatal explant model after 0, 6 and 18 h of culture. White dashed lines indicate the area of mesenchymal exposure. SB431542 (20 µM) and Pan-Ras-IN (20 µM) treatment completely inhibited the migration of MEE cells and subsequent mesenchymal exposure. (B) Frontal section of the palatal shelf of K14-GFP mice after 18 h of unpaired culture. E-cadherin expression is retained at the MEE region in both the SB431542-treated and Pan-Ras-IN-treated groups. Arrowheads indicate the mesenchyme exposure site. (C) Analysis of cell death after 24 h of palatal shelf organ cultures. The number of TUNEL-positive cells in remaining MEE cells (arrowheads) is markedly reduced in the Pan-Ras-IN-treated and SB431542-treated groups. (D) Analysis of cell proliferation after 24 h of palatal shelf organ culture. Proliferative activity is maintained in the remaining MEE cells (arrowheads) in the Pan-Ras-IN-treated and SB431542-treated groups. A, anterior; P, posterior. Scale bars: 200 μm (A,B); 100 μm (C,D). These experiments were performed at least three times with similar results.