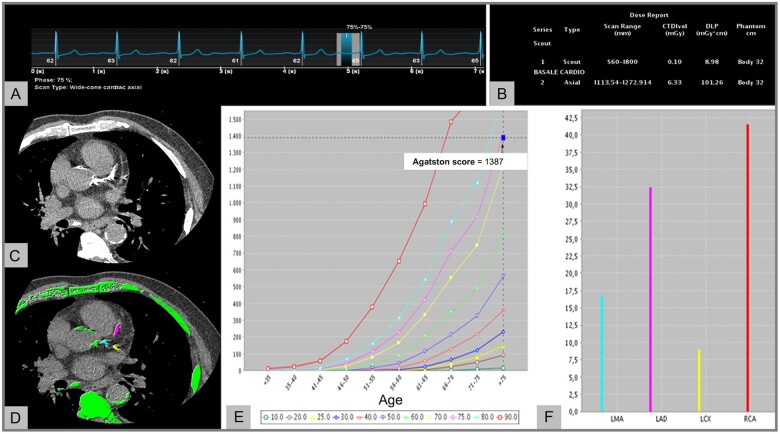
Figure 1.
Coronary artery calcium assessment. (A) A non-enhanced, ECG-triggered axial CT scan was acquired in a 78-year-old man to measure the calcific plaque burden. (B) Tube potential was set to 120 kV resulting into a total DLP of 101.26 mGy*cm. (C and D) Image analysis was performed using a dedicated software, which automatically identified structures with a density ≥130 HU and highlighted them in green. Subsequently, coronary arteries were manually segmented (LM: turquoise, LAD: pink, LCX: yellow). (E and F) Total Agatston score (E) and per-vessel Agatston score (F) were calculated and correlated to age-matched cohorts to stratify patient’s risk. ECG, electrocardiogram; CT, computed tomography; DLP, dose length product; LAD, left anterior descending artery; LCX, left circumflex artery; LM, left main.