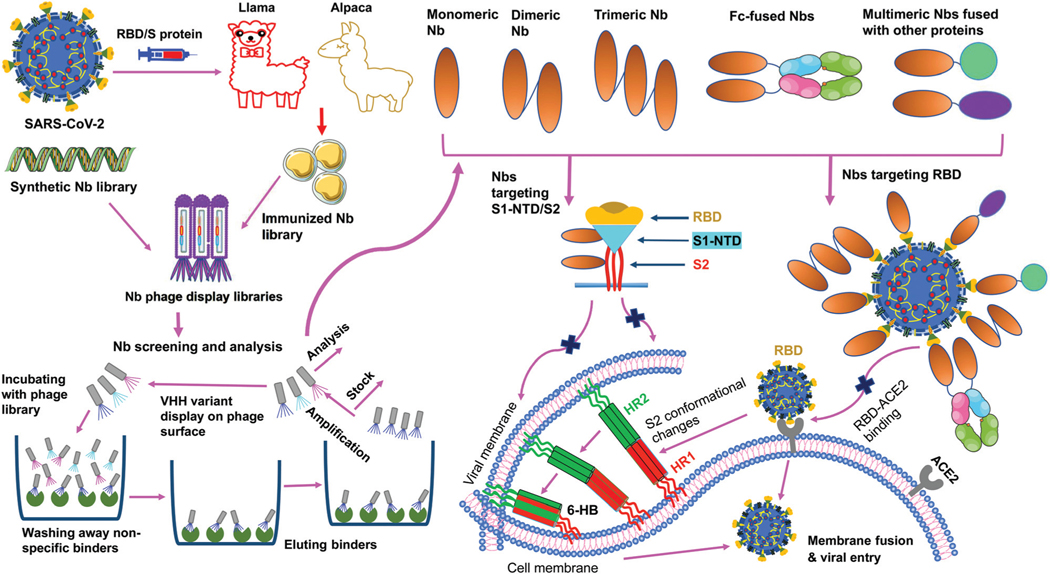
Fig. 4.
Generation and function of SARS-CoV-2-specific nanobodies. Nanobodies (Nbs) are generated by immunization of animals or screened from synthetic Nb phage display libraries. After a series of processes (incubation, wash, elution, amplification, and analysis), specific monomeric Nbs are screened; based on the identified monomeric Nbs, multimeric (dimeric, trimeric, Fc or other protein-fused) Nbs can be constructed. Nbs that target SARS-CoV-2 receptor-binding domain (RBD) in the spike (S) protein S1 subunit prevent the RBD-angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor binding, whereas Nbs that target N-terminal domain (NTD) in the S1 subunit (S1-NTD) or S2 subunit may inhibit the conformational changes of the S protein or S2-mediated membrane fusion, thereby preventing subsequent steps in viral infection. HR1 and HR2, heptad repeat 1 and 2; 6-HB, 6-helix bundle.