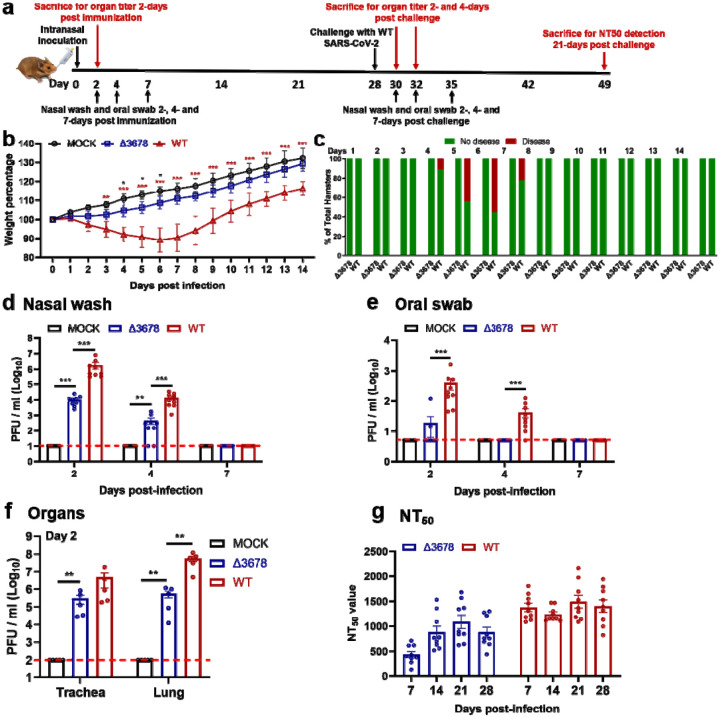
Figure 2. Attenuation of Δ3678 SARS-CoV-2 in hamsters.
a, Experimental scheme of Δ3678 virus immunization and WT virus challenge. Hamsters were intranasally (I.N.) inoculated with 106 PFU of WT or Δ3678 virus. On day 2 post-inoculation, organ viral loads (n=5) were measured by plaque assays on Vero-E6 cells. Nasal washes and oral swabs (n=10) were collected on days 2, 4, and 7 post-inoculation. On day 28 post-immunization, the hamsters were challenged by 105 PFU of WT SARS-CoV-2. On days 2 and 4 post-challenge, plaque assays were performed to measure organ viral loads (n=5). On day 21 post-challenge, the animals were terminated to measure neutralization titer (NT50). b, Weight changes of hamsters after intranasal infection with WT (n=9) or Δ3678 (n=9) SARS-CoV-2. Uninfected mock group (n=9) was included as a negative control. Body weights were measured daily for 14 days. The data are shown as mean ± standard deviation. The weight changes between Δ3678 and mock or WT groups were analyzed using two-factor analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Tukey’s post hoc test. The black and red asterisks stand for the statistic difference between Δ3678 and mock or WT, respectively. *, P<0.05; **, P<0.01; ***, P<0.001. c, Disease of Δ678 and Δ3678 virus-infected animals. The diseases include ruffled fur, lethargic, hunched posture, and orbital tightening. The percentages of animals with or without diseases are presented. d-f, Viral loads in nasal wash (d), oral swab (e), trachea, and lung (f) after infection with Δ3678 or WT virus. Dots represent individual animals (n=5). The mean ± standard error is presented. A non-parametric two-tailed Mann-Whitney test was used to determine the differences between mock, Δ3678, or WT groups. P values were adjusted using the Bonferroni correction to account for multiple comparisons. Differences were considered significant if p<0.025. *, P<0.025; **, P<0.005; ***, P<0.0005. g, Neutralization titers of sera from WT- and Δ3678 virus-inoculated hamsters on days 7, 14, 21, and 28 post-inoculation. The neutralization titers were measured against WT SARS-CoV-2.