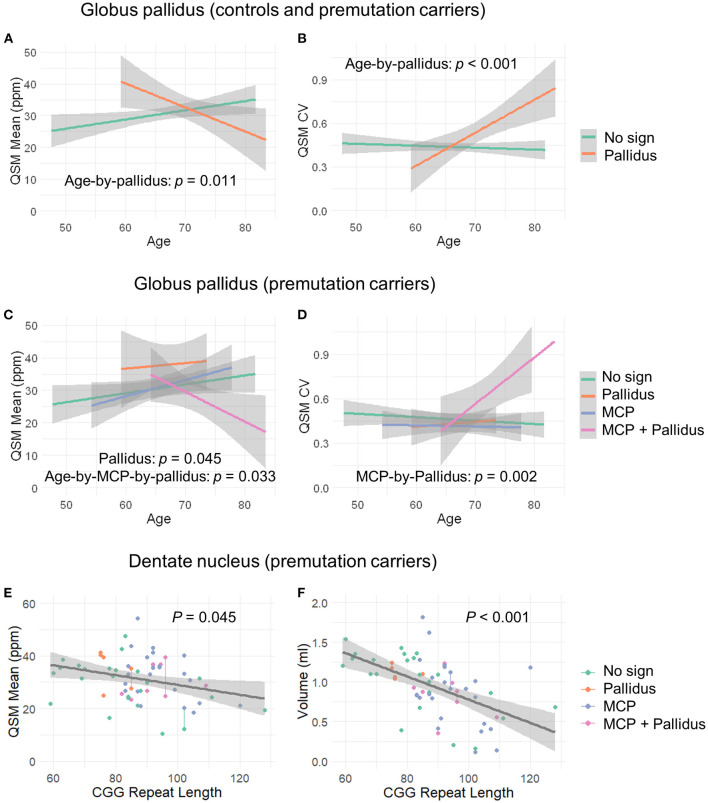
Figure 3.
The effect of MCP sign, pallidal T2-abnormalities, and CGG repeat length on the globus pallidus and dentate nucleus. (A) Age-related decrease in iron content in the globus pallidus for controls and premutation carriers with pallidal T2-abnormalities in contrast to age-related increase in iron content for those without the sign. (B) Age-related increase in iron variability in the globus pallidus for controls and premutation carriers with pallidal T2-abnormalities in contrast to non-significant age-related changes for those without the abnormalities. (C) Premutation carriers with pallidal T2-abnormalities showed increased iron in the globus pallidus compared to premutation carriers without the abnormalities, and premutation carriers with both pallidal and MCP T2-abnormalities showed decreased iron with age in the globus pallidus in contrast to the remaining premutation carriers who exhibited increased iron with age. (D) Premutation carriers with both pallidal and MCP T2-abnormalities revealed increased iron variability in the globus pallidus relative to the remaining premutation carriers. However, the apparent age-by-group interaction was not significant. (E) Negative correlation between CGG repeat length and iron content in the dentate nucleus in the premutation carriers. (F) Negative correlation between CGG repeat length and volume of dentate nucleus in the premutation carriers.