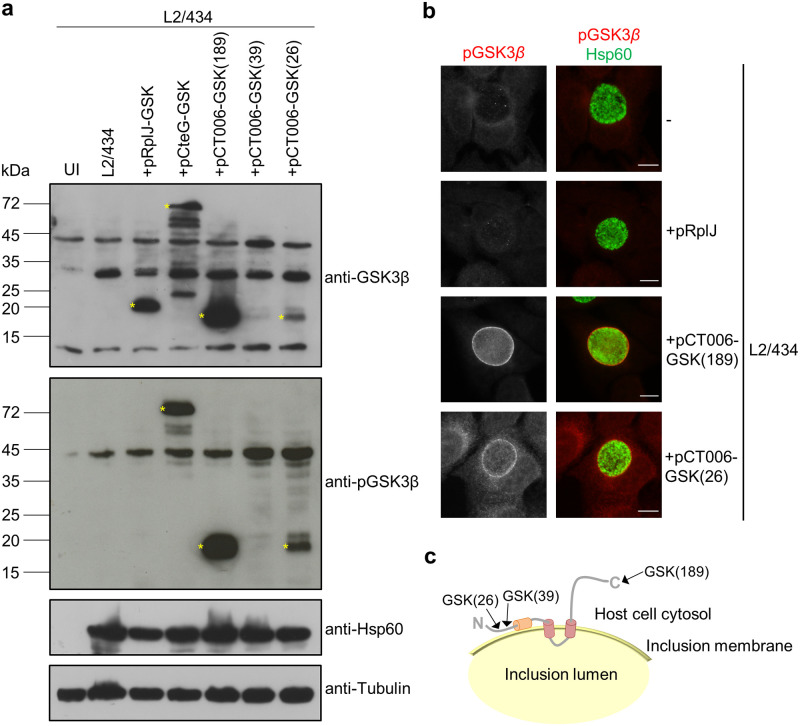
Fig 5. Analysis of the topology of CT006 at the inclusion membrane.
HeLa 229 cells were left uninfected (UI) or infected by C. trachomatis strains L2/434, L2/434+pRplJ-GSK, L2/434+pCteG-GSK, L2/434+pCT006-GSK(26), L2/434+pCT006-GSK(39) or L2/434+pCT006-GSK(189). (a) At 24 h post-infection, whole cell extracts were analyzed by immunoblotting using the antibodies anti-GSK3β, anti-phospho GSK3β (anti-pGSK3β), anti-C. trachomatis Hsp60 (bacterial loading control) and anti-α-tubulin (HeLa 229 cells loading control) and the appropriate horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-conjugated secondary antibodies, followed by detection using SuperSignal West Femto (GSK and pGSK) or SuperSignal West Pico detection kit (Hsp60 and tubulin) (Thermo Fisher Scientific). (b) At 24 h post-infection, cells were fixed with 4% (w/v) PFA, immunolabeled with anti-pGSK3β (red) and anti-Hsp60 (green), and appropriate fluorophore-conjugated secondary antibodies. The labeled cells were then imaged by fluorescence microscopy. Scale bars, 10 μm. (c) Schematic representation of the deduced topology of CT006 at the inclusion membrane. The arrows indicate the position where the GSK tag was fused. The analysis with the GSK tag showed that the putative hydrophobic domain of CT006 between amino acid residues 47 and 69 (in orange) does not cross the inclusion membrane.