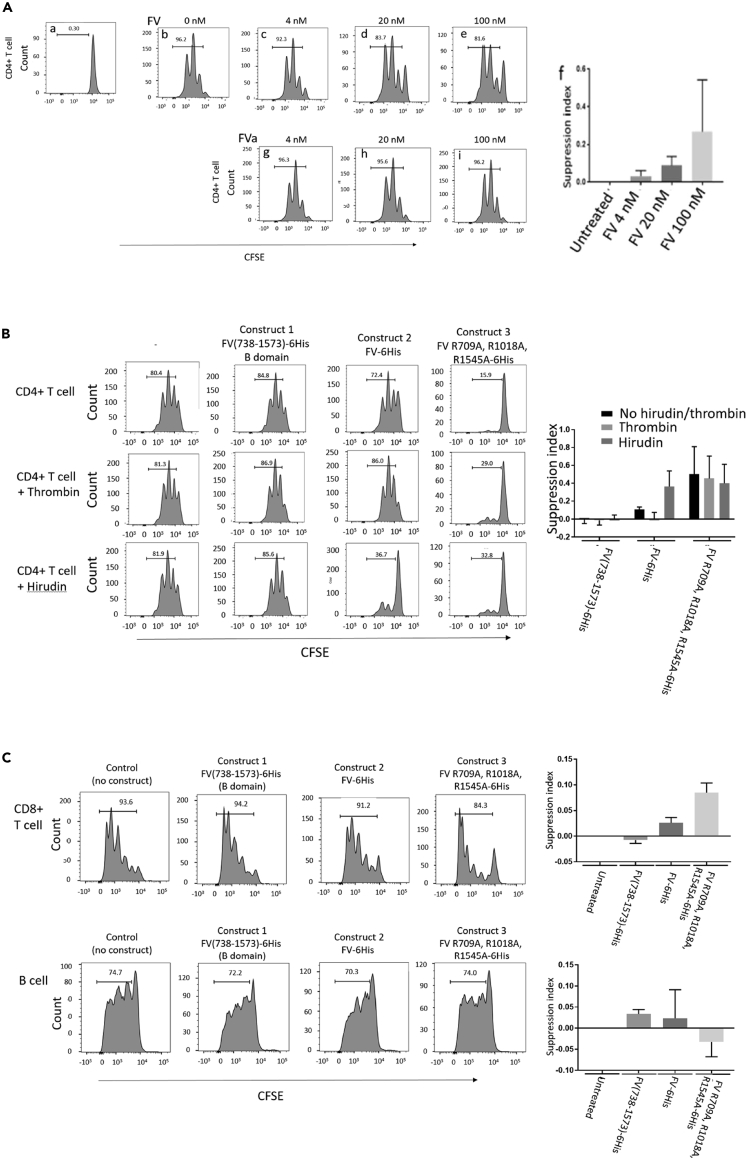
Figure 3.
FV but not FVa suppresses T-cell proliferation in vitro
(A) CD4+T conventional cells (Tcon) labeled with carboxyfluorescein diacetate succinimidyl ester (CFSE) (A), were stimulated with Dynabeads T-cell activator. Proliferation dilutes the dye, reducing fluorescence intensity with each cycle of cell division (B). Proliferation is inhibited in a concentration dependent manner by native Factor V (panels c – e), but not FVa (G – I).Data are representative of 10 healthy donors, and presented as mean and SEM (F). FV induced a significant suppression of T-cell proliferation in a concentration dependent manner: 4nM FV versus control p = 0.0077; 20 nM versus control p = 0.0003; 100 nM versus control p = 0.013. Bar chart shows mean and SEM.
(B) CD4+ Tcon proliferation was not inhibited by recombinant FV B domain (Construct 1, 20 nM), and thrombin and hirudin had no effect on their own and in combination with construct 1. Recombinant full length Factor V (construct 2, 20 nM) inhibited CD4+ Tcon proliferation similar to native plasma derived Factor V, and its effect was prevented by thrombin (p = 0.036), while the effect of inhibition by mutated Factor V (construct 3, 20 nM) was not prevented by thrombin (p = 0.25). Data are representative of three healthy donors. Bar chart shows mean and SEM
(C) CD8+T-cell proliferation was inhibited similarly by 20 nM construct 2 (p = 0.009) and construct 3 (p = 0.004), while B cell proliferation was not inhibited by any of the constructs (p = 0.1; p = 0.3; p = 0.6). Pro: proliferation. CD8+data are representative of four healthy donors, and B cell data are representative of three healthy donors. Bar chart shows mean and SEM.