Fig. 4.
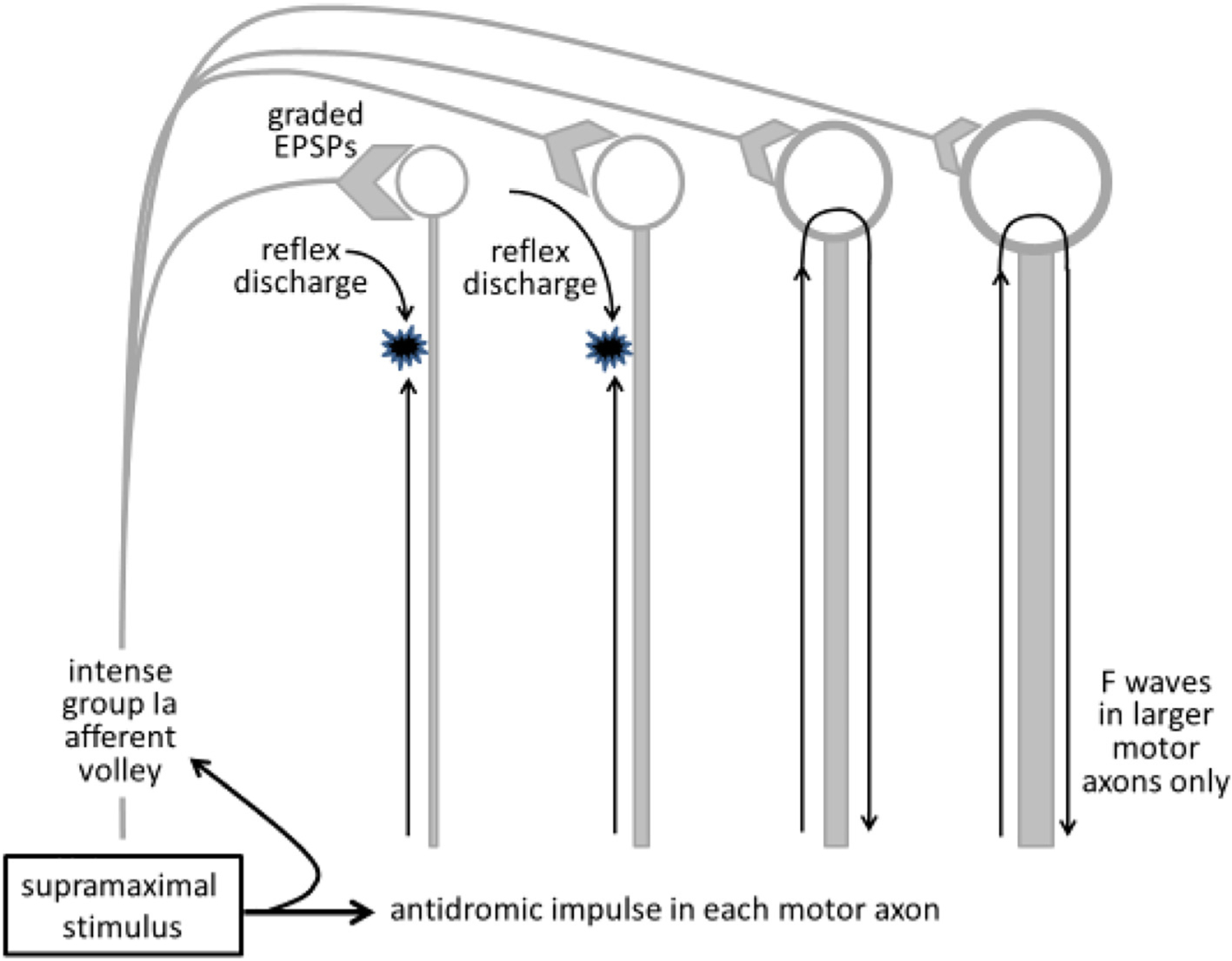
Reflexly activated motoneurons cannot produce F waves. In human subjects, the supramaximal stimulus necessary for F wave studies will produce an intense afferent volley. If motoneurons are activated by this afferent input, the reflex discharge will collide with the antidromic volley in motor axons, thus preventing the antidromic invasion of those motoneurons (the two motoneurons on the left). As a result, F waves will occur only for higher-threshold motoneurons that have a smaller compound excitatory post-synaptic potential (EPSP) and do not discharge reflexly in response to the afferent volley. From (Mills, 2017) with permission.
