Figure 5:
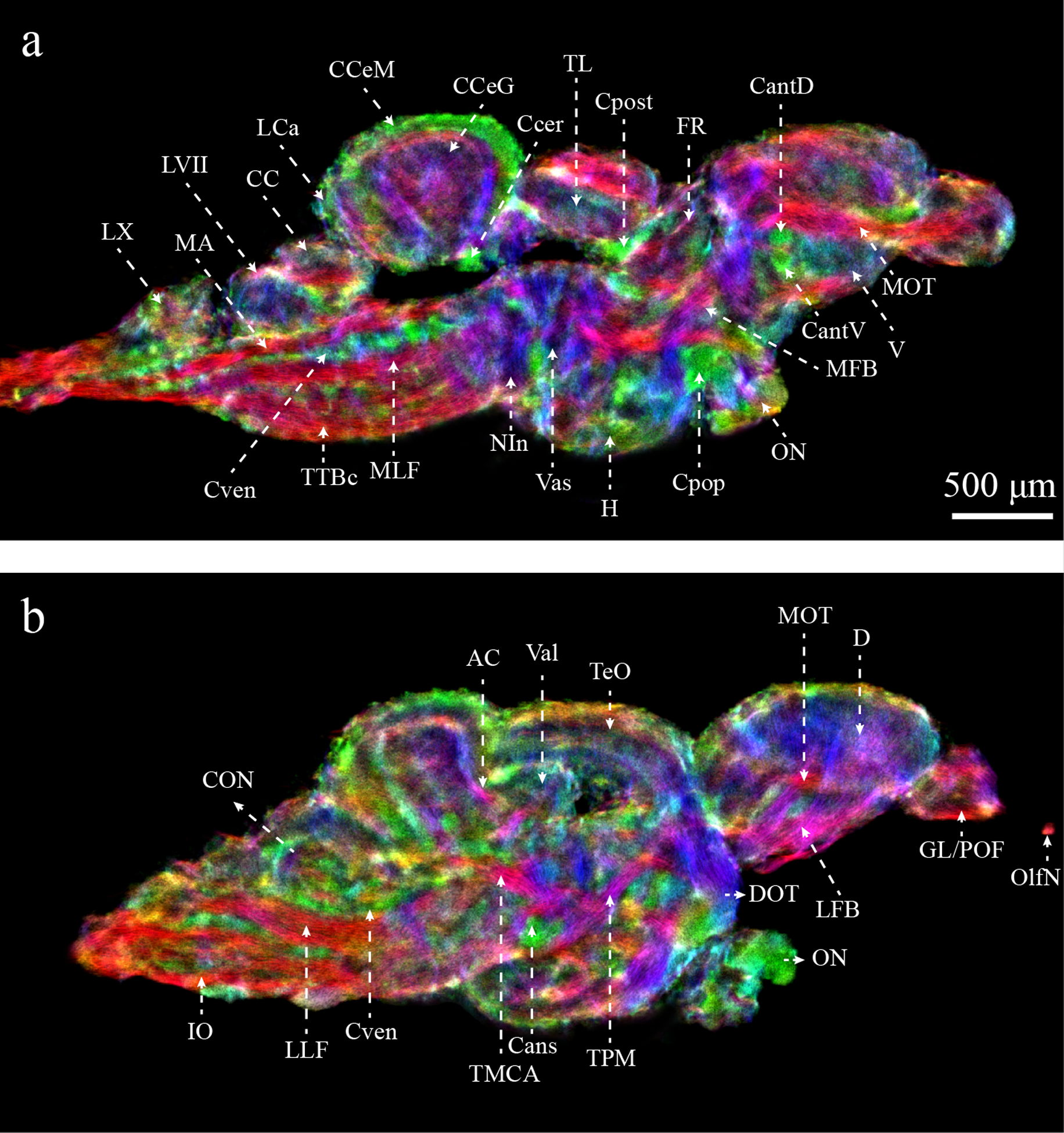
Enhanced characterization of the zebrafish brain from DEC-stTDI images (5μm isotropic resolution). Identified structures include: AC, anterior cerebellar tract; Cans, ansulate commissure; CantD, anterior commissure, dorsal part; CantV, anterior commissure, ventral part; CC, cerebellar crest; CCeG, cerebellar corpus, granular layer; CCeM, cerebellar corpus, molecular layer; Ccer, cerebellar commissure; CON, caudal octavolateralis nucleus; Cpop, postoptic commissure; Cpost, posterior commissure; Cven, ventral rhombencephalic commissure; DOT, dorsomedial optic tract; FR, habenula-interpeduncular tract; GL/POF, glomerular/primary olfactory layers; IO, inferior olive; LCa, caudal lobe of the cerebellum; LFB, lateral forebrain bundle; LLF, lateral longitudinal fascicle; LVII, facial lobe; LX, vagal lobe; MA, Mauthner axon; MFB, medial forebrain bundle; MLF, medial longitudinal fascicle; MOT, medial olfactory tract; NIn, interpeduncular nucleus; OlfN, olfactory nerve; ON, optic nerve; TeO, optic tectum; TL, longitudinal torus; TMCA, anterior mesencephalon-cerebellar tract; TPM, pretecto-mammillary tract; TTBc, crossed tecto-bulbar tract; Val, lateral division of the valvula cerebelli; Vas, vascular lacuna of area postrema. Color-coding indicates the local orientation (red: rostral-caudal, green: medial-lateral, blue: dorsal-ventral).
