Figure 4.
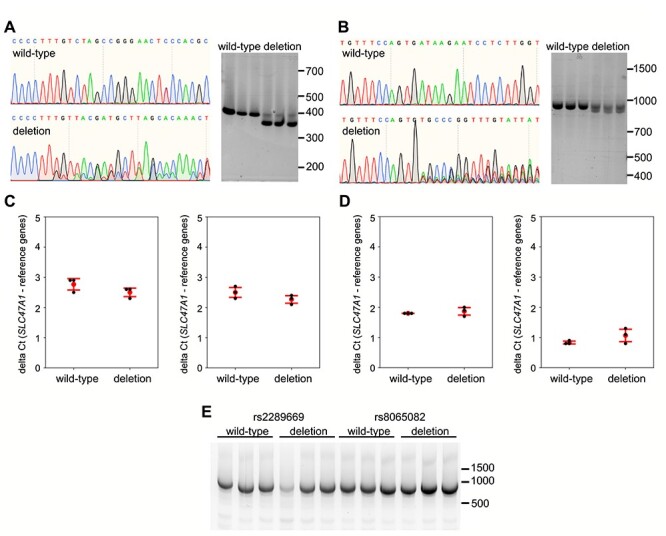
Assessment of effect on splicing and SLC47A1 expression after deletion of genomic DNA around rs2289669 and rs8065082 in HepG2 cells. (a, b) Representative Sanger sequencing traces of HepG2 genome at rs2289669 locus (a) and at rs8065082 locus (b), before (wild-type) and after CRISPR-Cas9-mediated deletion (deletion). Right panels in each subfigure show agarose-gel images of PCR amplicons of the respective loci before (wild-type) and after deletion (deletion), generated from three biological replicates. (c, d) qPCR for SLC47A1 on cDNA from wild-type cells versus cells with rs2289669 deletion (c) or rs8065082 deletion (d). Probes against two different exon boundaries of the SLC47A1 transcript were used (exons 1–2 on the left, and exons 14–15 on the right in each subfigure). Graphs show mean delta Ct (red dot) and standard deviation (red error bars), and also individual biological replicates’ mean Ct values obtained from three technical replicates (black dots). Mann–Whitney U test was used to calculate P-values, with no statistical significance obtained in all tests. e) Qualitative assessment of splicing of SLC47A1 transcripts covering the range of exons 5–17. RNA from three biological replicates each of wild-type versus deletion-carrying cell populations was used to run one-step end-stage RT-PCR.
