Figure 1.
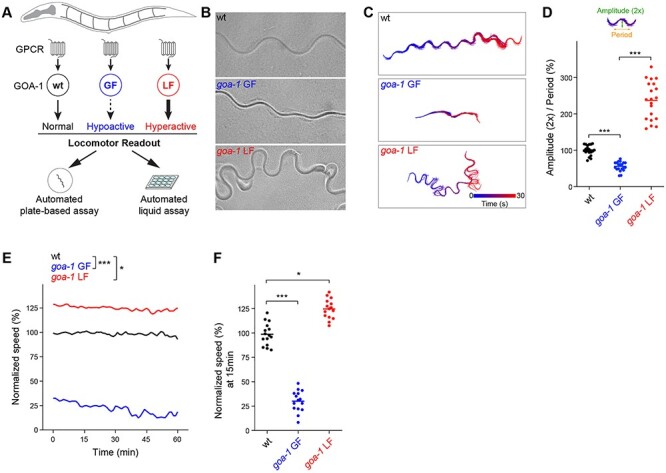
Automated behavioral tracking indicates that canonical goa-1 LF and GF mutants have opposing locomotor defects. (A) Schematic showing GOA-1/Gαo function in C. elegans locomotion and design of automated behavioral paradigms. (B) Representative images of C. elegans wave form traces in plate-based locomotion assays for indicated genotypes. (C) Representative traces of locomotor waveforms acquired using automated behavioral tracking for indicated genotypes. (D) Quantitation of locomotor waveforms for indicated genotypes (n = 20 animals per genotype). Shown are parameters (2× amplitude and period) used for quantitative analysis. (E) Time course of automated tracking in liquid locomotor assays for indicated genotypes (n = 15 wells; 60 ~ 75 total animals per genotype). (F) Quantitation of mean speed (line) and speed per well (circles) after 15 min of automated tracking for each genotype (n = 15 wells; 60–75 animals per genotype). In all cases, mean speed was calculated every minute for each well and normalized to wild type for baseline locomotion (5 min) and for body size. For panels D and F, comparisons represent one-way ANOVA followed by post hoc Bonferroni's test. For panel E, comparisons represent two-way ANOVA followed by post hoc Bonferroni's test. *P < 0.05, ***P< 0.001.
