Figure 3.
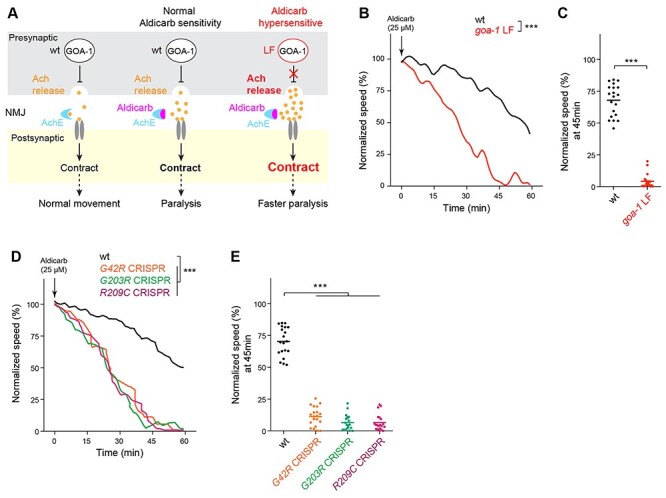
GNAO1 pathological mutations cause loss of function effects during pharmacological manipulation of the C. elegans motor circuit. (A) Diagram illustrating pharmacological manipulation of the C. elegans motor circuit using the acetylcholinesterase inhibitor aldicarb (left, middle). goa-1 LF increases excitatory Ach release in the C. elegans motor circuit resulting in hypersensitivity to aldicarb (right). (B) Automated aldicarb assay shows canonical goa-1 LF mutants are hypersensitive to aldicarb. Arrow indicates drug application. (C) Quantitation of mean speed (line) and speed per well (circles) after 45 min of tracking in automated aldicarb assays for indicated genotype. (D) Automated aldicarb assays show three CRISPR edited mutants that are homozygous for GNAO1 pathological mutations (G42R, G203R, R209C) display aldicarb hypersensitivity. (E) Quantitation of mean speed (line) and speed per well (circles) after 45 min of tracking in automated aldicarb assays for indicated genotypes. In all cases, mean speed was calculated every minute for each well and normalized to baseline locomotion (10 min prior to addition of aldicarb) for each genotype. For panels B and D, comparisons represent two-way ANOVA followed by post hoc Bonferroni's test. For panel C, comparison represents two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test. For panel E, comparisons represent one-way ANOVA followed by post hoc Bonferroni's test. For all experiments, n = 20 wells; 80 ~ 100 animals per genotype. ***P < 0.001.
