Figure 4.
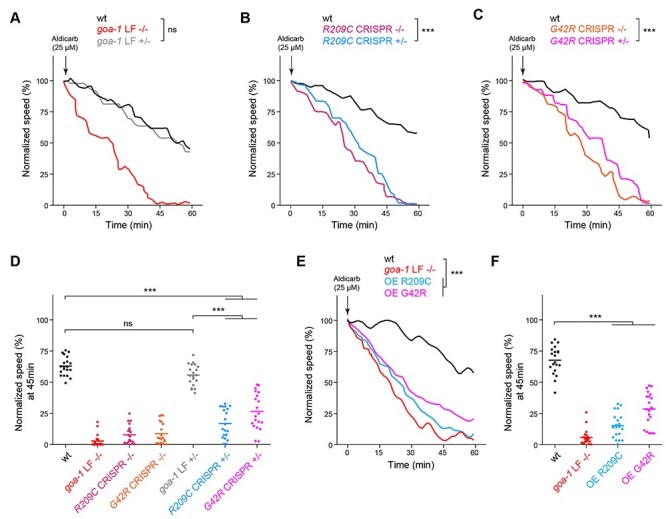
Multiple genetic approaches demonstrate GNAO1 pathological mutations functions as dominant negative alleles in C. elegans. (A) Automated aldicarb assay showing homozygous animals carrying a goa-1 LF null allele are hypersensitive to aldicarb. In contrast, heterozygous goa-1 LF+/− animals show normal aldicarb responses compared to wild type. (B) Automated aldicarb assays show both heterozygous and homozygous goa-1 R209C CRISPR mutants are hypersensitive to aldicarb. (C) Automated aldicarb assays show both heterozygous and homozygous goa-1 G42R CRISPR mutants are hypersensitive to aldicarb. (D) Quantitation of mean speed (line) and speed per well (circles) after 45 min of tracking in automated aldicarb assays for indicated genotypes. (E) Automated aldicarb assay showing transgenic overexpression of GOA-1 R209C and G42R induce aldicarb hypersensitivity. (F) Quantitation of mean speed (line) and speed per well (circles) after 45 min of tracking in automated aldicarb assays for indicated genotypes. In all cases, mean speed was calculated every minute for each well and normalized to baseline locomotion (10 min prior to addition of aldicarb) for each genotype. For E and F, data shown is from 5 transgenic lines for each genotype. Data for individual transgenic lines is shown in Supplementary Material, Fig. S3. For panels A-C and E, comparisons represent two-way ANOVA followed by post hoc Bonferroni's test. For panels D and F, comparisons represent one-way ANOVA followed by post hoc Bonferroni's test. For all experiments, n = 20 wells; 80–100 animals per genotype. ***P < 0.001.
