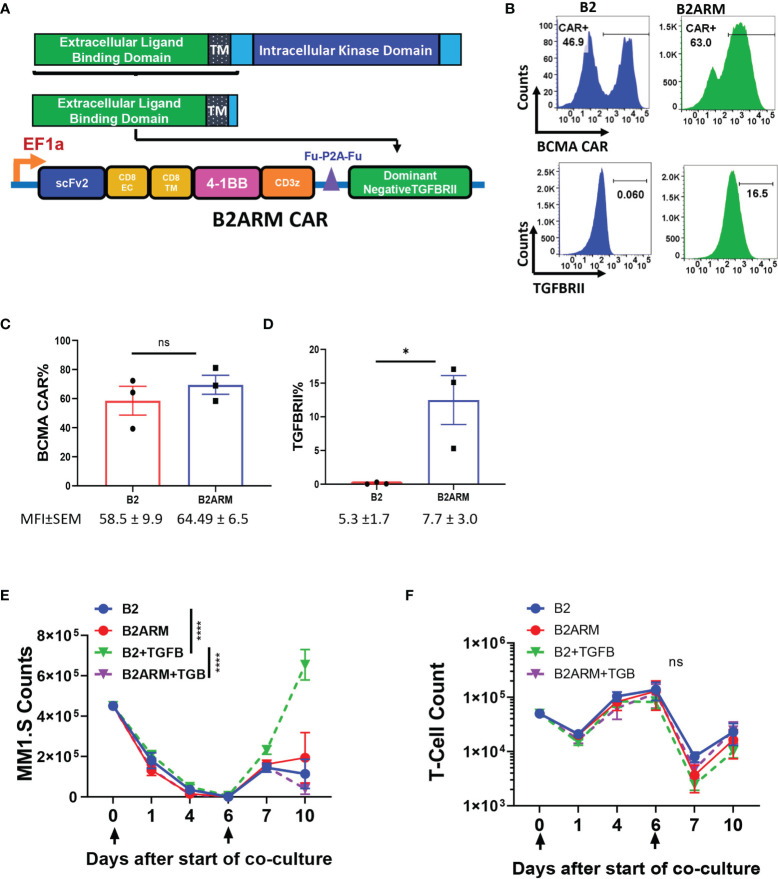
Figure 3.
The B2ARM T-cells with the truncated TGFBRII dominant negative receptor are resistant to the suppressive effects of TGF-β. (A) To create the armored B2ARM BCMA CAR, the sequence of the extracellular and transmembrane domains of TGFBRII, excluding the intracellular kinase domain, was cloned in frame downstream of the B2 CAR construct. (B) T-cells were transduced with lentiviral vectors containing either the B2 CAR construct at MOI 10, or the B2ARM construct at MOI 80, in order to compensate for the lower transduction efficiency of the armored B2ARM CAR construct, which is larger. The cell surface expression of the BCMA CAR (upper panel) and TGFBRII (lower panel) was assessed by flow cytometry. One representative donor is shown. (C) Pooled results from transduction experiments with B2 and B2ARM constructs showing the expression of (C) the CAR and (D) the TGFBRII armor in T cells from three separate donors, mean ± SEM. *p<0.05, Student t-test, ns, non-significant. Mean ± SEM of mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) values for each experimental group are shown below the figures. In the long term co-culture experiment, CAR T-cells were co-incubated with the target cells, MM.1S-GFP, at an ETT ratio of 0.1, and the culture was treated with 10ng/ml of TGF-beta or remained untreated. When less than 15% of target cells remained on day 6, the co-culture was extended for a second round by adding the co-culture cells from the previous round to fresh target cells. The absolute counts of (E) T-cells and (F) target cells at different time points during the long-term co-culture was assessed by quantifying the number of CD3+ and GFP+ cells via flow cytometry using absolute counting beads. Data represent mean ± SEM of separate long term experiments performed in T cells from three different donors. Statistical analysis was performed by two way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test, ****p<0.0001.